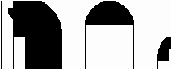
U of MN Questions
1-6. Match the surgical procedure with the anatomic hook-up:
1. Glenn A. SVC to PA
2. Fontan B. RA to PA
3. Blalock-Taussig C. RV to PA
4. Rastelli D. Ascending aorta to PA
5. Waterston E. Descending aorta to PA
6. Potts F. Subclavian artery to PA
7-11. Regarding true and false aneurysms of the left ventricle, match the following:
7. Associated with cardiac tamponade
8. Associated with calcification
9. Located posteriorly along the diaphragm
10. Can be surgically repaired
11. Associated with atherosclerotic disease
A. True aneurysms only
B. False aneurysms only
C. Both true and false aneurysms
D. Neither true nor false aneurysms
12-14. Match the following pressure tracings:
A. Subaortic stenosis
B. Coarctation of aorta
C. PV stenosis
D. Aortic regurgitation
E. Aortic stenosis
12. Pressure
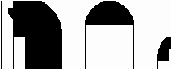
PV RV
13. Pressure
LV Aorta
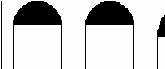
14. Pressure

LV Aorta
15. The most common cause for cyanosis and increased pulmonary vascularity in a newborn:
A. Transposition
B. Tetralogy of Fallot
C. PV atresia
D. Tricuspid atresia
E. TAPVR
F. Epstein's
16. Regarding GI bleeding studies (Single best answer):
A. Need at least 1.5 ml/min blood loss for a tagged RBC study to detect a bleed
B. Tagged RBC study is about as sensitive as a sulfur colloid study
C. Twenty-four hour image in a tagged RBC study is useful to see the appearance of movement of tracer
D. To identify a GI bleed, you must see tracer in the lumen and movement of the tracer
17. The left gastroepiploic artery is a branch of the:
A. Splenic artery
B. Gastroduodenal artery
C. Superior mesenteric artery
D. Right gastric artery
E. Left gastric artery
F. Celiac artery
18-19. True/False - Regarding aortic dissection:
18. MRI is the imaging study of choice
19. The false lumen does not fill with contrast on CT
20-24. True/False - Regarding FMD of the carotid artery:
20. The internal carotid is affected more frequently than the external carotid
21. The false lumen does not fill on angiography
22. You see a string of beads sign on angiography
23. The intracranial vessels are also affected
24. It is usually unilateral
25-27. True/False - Regarding arterial stenting:
25. It is the treatment of choice for dissection after PTCA
26. The size of the balloon is indicated by the severity of stenosis
27. It is indicated for popliteal and perineal artery stenosis
28-29. True/False - Patient with 7.5 cm AAA:
28. His cumulative risk for rupture over 5 years is 95%
29. Bilateral renal artery involvement is a contraindication for repair
30-34. Matching:
30. Fontan A. Subclavian artery PA
31. Potts B. Rt. atrium PA
32. Blalock-Taussig C. Ascending aorta PA
33. Waterston D. Descending aorta PA
34. Glenn E. Superior vena cava PA
35. Least likely to be involved by aortic dissection (Single best answer):
A. Left renal artery
B. Left subclavian artery
C. Left iliac
D. Right carotid
E. Left coronary
36-39. True/False - Concerning percutaneous transluminal angioplasty:
36. Following angioplasty of iliac artery with formation of dissection, stent placement is indicated
37. Following unsuccessful angioplasty of a popliteal stenosis, stent placement is indicated
38. Choice of balloon diameter used depends on degree of stenosis
39. A patient with pain one hour post angioplasty indicates complication
40-42. Match:
40. Plasma oncotic pressure
41. Mean pulmonary arterial pressure
42. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
A. 5 mm Hg
B. 10 mm Hg
C. 15 mm Hg
D. 20 mm Hg
E. 25 mm Hg
F. 30 mm Hg
43. Mean pulmonary artery pressure is:
A. 10
B. 15
C. 20
D. 25
E. 30
44-46. True/False - Regarding AAA:
44. More common in African-American patients
45. More common in Caucasian males vs. Caucasian females
46. >95% rupture if >5 cm
| Note - Questions 47-91: If a statement is determined to be true only rarely, it is labeled as "False", but noted that it is rarely true. |
47-48. True/False - Regarding cardiovascular MRI
47. Flow in wrong direction through valve may be seen as black flow jet
48. EKG gating not necessary
49-50. Match the following with the opposite effect:
49. Priscoline and ergotamine
50. Vasopressin and nitroglycerine
51-54. True/False - Which of the following veins have the valves?
51. Azygous vein
52. Coronary vein
53. Cephalic vein
54. Spermatic vein
55. In a patient with an aortic dissection, which vessels are affected? (Basically, know where the false lumen is in an aortic dissection, which is described in Dahnert)
A. Left coronary artery
B. Left renal artery
C. Left iliac artery
D. ...
E. ...
56-58. True/False - Regarding aneurysms of LV:
56. Rim calcification
57. Posterior next to diaphragm
58. Could cause rupture and tamponade
59. True/False - In a trauma patient, displacement of the nasogastric tube on a chest x-ray is sensitive or specific for aortic transection.
60. On high-resolution CT of the chest, LAM most closely resembles : lymphangioleiomyomatosis
A. Sarcoid
B. Pan lobular emphysema
C. Centrilobular emphysema
D. Eosinophilic granuloma
E. ...
61-65. True/False - Regarding surfactant:
61. Increases alveolar wall tension
62. Produced by Type II pneumatocytes
63. Used to treat meconium aspiration
64 Cells that produce it connected by bars
65. Produced by Type I pneumocytes
66-74. Pulmonary function test diagram - asked to label:
66. FVC = FVC = (Forced) Vital Capacity
67. TLV =
68. ERV = Expiratory Reserve Volume
69. TV = Tidal Volume
70. RV = Residual Volume
71. FRC = Functional Residual Capacity
72. TLC = Total Lung Capacity
73. IC = Inspiratory Capacity
74. EC = Expiratory Capacity (not a usually defined volume)
See diagram below:
75. The most likely cause for bilateral diffuse, granular infiltrate in an 8-year-old with AIDS without symptoms is:
A. PCP
B. Lymphoma
C. Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
D. MAI
E. ...
76-79. True/False - Regarding Kaposi's sarcoma of the lung:
76. Usually asymptomatic
77. Often a presenting problem with HIV patients
78. May present with sudden shortness of breath, infiltrates on chest x-ray
79. Often precedes cutaneous Kaposi's
80-83. True/False - Cystic fibrosis patients get pneumonia from:
80. Pseudomonas
81. Klebsiella
82. Staph aureus
83. Strep viridans
84. HIV+ patients with painful erythematous skin papules and lytic tibial lesion (Single best answer):
A. Cat scratch dz (bacillary angiomatosis)
B. Kaposi's
C. Coccidioidomycosis
D. ...
E. ...
85. Pattern of pulmonary edema when trachea is acutely obstructed (Single best answer):
A. Basilar predominance
B. Perihilar
C. Diffuse
D. With pleural effusions
E. Central
F. Peripheral
G. Upper lobe
H. Lower lobe
86. Matching with Swan-Ganz catheter tracings.
87-91. True/False - Wegener's granulomatosis:
87. Commonly presents with renal disease
88. More commonly affects adults than children
89. Commonly presents with lung and parasinus disease
90. Most patients get cavitary lung lesions
91. Commonly cavitates, presents with renal failure
92. Which is least likely to present with upper lobe disease? (Single best answer):
A. Silicosis
B. EG
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Asbestosis
E. Ankylosing spondylitis
93. What is lymphangioleiomyomatosis most similar to?
A. IPF
B. Eosinophilic granuloma
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Panlobular emphysema
E. Centrilobular emphysema
F. Panacinar emphysema
94-98. Matching - Concerning the pulmonary interstitia:
94. Ground glass
95. Kerley A
96. Kerley B
97. Visceral pleural thickening
98. Peribronchial thickening
A. Central
B. Peripheral
C. Parenchymal
101-105. True/False - Regarding evaluation of cardiac silhouette on apical lordotic chest x-ray
101. The apex appears elevated
102. The right heart border is more prominent
103. The heart appears enlarged
104. The aortic arch is more prominent
105. The pulmonary artery segment is less prominent
106. Exudative pleural effusion (Single best answer):
A. Cirrhosis
B. Neoplasm
C. Nephrotic syndrome
D. Congestive heart failure
E. ...
107. Concerning pulmonary function tests - Know the definition of functional residual capacity, residual volume, vital capacity.
108-109. True/False - Concerning bleomycin toxicity on the lung:
108. There is a synergistic effect of oxygen and bleomycin
109. There is a synergistic effect of radiation therapy and bleomycin
110. True/False - Type II pneumocytes can regenerate.
111. True/False - Type I pneumocytes can regenerate.
112. Know the appearance of the heart, aorta, and pulmonary artery on an apical lordotic film. What gets magnified on an apical lordotic film? What happens to the appearance of the right atrium -- Does it get larger or smaller?
113-116. Match:
113. Upper lung
114. Lower lung
115. Middle lung
116. Central airways
A. Silicosis
B. Centrilobular emphysema
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Asbestosis
E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
117-120. Match:
117. Sickle cell A. Pseudomonas
118. Silicosis B. Pneumococcus
119. Sarcoidosis C. Tuberculosis
120. Cystic fibrosis D. Aspergillosis
121-123 . True/False - Cystic fibrosis
121:is associated with esophageal reflux.
122. patients are prone to develop intussusceptions.
123. patients are prone to develop mechanical obstructions.
124. Increased compliance of lung:
A. IPF
B. Alpha-1 antitrypsin
C. CHGF
D. ...
E. ...
125-127. Match the following, regarding ultrasound:
125. Mirizzi's syndrome
126. Kawasaki's disease
127. Adenomyomatosis
A. Hydrops of the gallbladder
B. Bulky lymph nodes in the portocaval region
C. Segmental thickening of the gallbladder wall
D. Nonshadowing mass protruding into the gallbladder lumen
E. Cystic duct stone and intrahepatic biliary dilatation
128. A 35-year-old male with hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis and hypertension most likely has:
A. Adrenal adenoma
B. Pheochromocytoma
C. Pancreatic islet cell tumor
D. Metastases to the liver
129-131. Regarding the colon, match the following:
129. Lymphogranuloma venereum
130. Amebiasis
131. Bechet's disease
A. Aphthous ulcers
B. Fistulas
C. Granular mucosa
D. Toxic megacolon
132-134. Match:
132. Uncinate process
133. Caudate lobe
134. Right renal artery
A. Lateral to IVC
B. Cephalad to portal vein
C. Posterior to SMV
D. Posterior to IVC
E. Caudal to portal vein
135. The most common complication of adrenal gland biopsy:
A. Hemorrhage
B. Pneumothorax
C. Tumor seeding biopsy tract
D. Pancreatitis
136-138. Match:
136. Divides medial and lateral segments of the left lobe of the liver
137. Divides the right lobe into anterior and posterior segments
138. Divides the right and left lobes of the liver
A. RHV
B. MHV
C. Ligamentum teres
D. Falciform ligament
139-142. True/False - Regarding acute pancreatitis:
139. 4 cm fluid collection must be surgically drained or interventionally (radiology) drained
140. Ranson criteria of 7 means a good prognosis
141. Contrast-enhanced CT scan can be used to determine the extent of pancreatic necrosis
142. Long-segment stricture of the CBD may be a sequelae
143. A young female adult with diarrhea, malabsorption and transient intussusceptions. Most likely cause:
A. Whipple's disease
B. Jejunal adenocarcinoma
C. Pancreatitis
D. Sprue
144. Necrolytic erythema migrans (Single best answer):
A. Glucagonoma
B. VIPoma
C. Insulinoma
D. Somatostatinoma
E. Gastrinoma
145-147. Matching:
145. Diarrheogenic
146. Bradykinin
147. Calcitonin
A. Carcinoid
B. MEN III
C. VIPoma
148. The esophagus does not have a (Single best answer):
A. Serosa
B. Mucosa
C. Longitudinal muscle layer
D. Circular muscle layer
E. Muscularis mucosa
149. Most common presentation in an adult of a small amount of free intraperitoneal air on a supine film:
A. Rigler's sign
B. Falciform ligament
C. Umbilical ligament
D. Cupola sign
E. Free air at edge of liver
150-153. True/False - Concerning internal hernias:
150. Right greater than left
151. Inframesocolic greater than supramesocolic
152. Transmesenteric more common in adults than in children
153. Right internal hernia travels through the foramen Landzert
154-156. True/False - Concerning FNH:
154. Is associated with oral contraceptives
155. Hemorrhage
156. Malignant transformation
157. Know the cause of isolated gastric varices.
158. There was a question concerning desmoplastic fibroma.
159. True/False - Celiac sprue is associated with lymphoma.
160-161. True/False - Concerning Ranson's criteria for pancreatitis:
160. A low score has a bad prognosis
161. A high score has a bad prognosis
162. Know the appearance of a biliary cystadenoma.
163. True/False - Whipple's disease is associated with arthritis.
164. True/False - Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is associated with non-Beta cell tumors.
165. True/False - Typhlitis is associated with immunocompromised patients.
166. Know the division of the lobes of the liver and what divides them.
167-171. True/False - Indications for percutaneous renal stone removal:
167. Staghorn calculus
168 Stone <2-3 cm
169. Cysteine stone
170. Stone in a child
171. Uteropelvic obstruction
172. A 28-year-old post-partum female presents with acute left flank pain. Outpatient IVP was negative. The next day, a scout film for a barium enema shows contrast retained in bilateral, dilated kidneys. No contrast is present in the collecting systems. The patient probably has:
A. Acute tubular necrosis
B. Acute bilateral pyelonephritis
C. Contrast-induced renal failure
173. An eight-year-old girl with a urinary tract infection and left flank pain. Initial imaging study should be:
A. Ultrasound
B. CT scan
C. MRI
D. VCUG
E. IVP
174. Which of the following is NOT true regarding percutaneous nephrostomy:
A. The tube should be removed over a wire
B. Infection of the bladder results in more complications
C. Puncture should be made into the anterior calyx
D. It is the treatment of choice for pyonephrosis
E. On an AP film, the posterior calices are seen end-on
175-179. Match the property of IV contrast to its side effect:
175. Osmolality A. Peripheral vasodilation
176. Increased Na+ B. Cardiac arrhythmia
177. Ionicity C. Crosses blood-brain barrier
178. Na content D. Hypertension
179. Nonorganic iodine E. Anticlotting action
F. Deformed RBC
G. Alteration of BBB
H. Increased parotid gland
180-185. True/False - Regarding malakoplakia:
180. Most often affects the bladder
181. Is premalignant
182. Associated with E. coli infection
183. Increased incidence with HIV infection
184. More commonly involves ureter than bladder
185. Is associated with diabetes
186. Lateral deviation of the uterus at the level of the pelvic brim - on an IVP is most likely associated with:
A. AAA
B. Retroperitoneal fibrosis
C. Pelvic lipomatosis
D. Retroperitoneal bleed
E. Retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy
187-190. Match the cysts with their location.
187. Utricle A. Midline
188. Seminal vesicle B. Para-median (near midline)
189. Ejaculatory duct C. Lateral
190. Müllerian duct
191. A 38-year-old male with a long-segment stricture of the bulbous urethra shows filling of the glands of Littre on a retrograde urethrogram. Most likely cause:
A. Transitional cell carcinoma
B. Gonorrhea
C. Straddle injury
D. Pelvic ring fracture
192. Salpingitic isthmica nodosa is most strongly associated with:
A. Uterine synechia
B. Endometriosis
C. Adenomyosis
D. Endometrial thickening
E. Hydrosalpinx
F. Endometrial hyperplasia
G. Sinequia
193-197. True/False - Regarding endometrial thickening:
193. Best measured in the coronal plane
194. Noncyclical bleeding can occur with thickening <4 mm
195. A polyp can simulate endometrial thickening
196. Tamoxifen acts as an anti-estrogen
197. Estrogen can cause thickening
198-201. Match the following regarding the placenta:
198. Accretia A. Invades the myometrium
199. Incretia B. Adjacent to the myometrium
200. Percretia C. Perforates the myometrium
201. Myocretia
202. Most common place prostate cancer is found (Single best answer):
A. Central zone
B. Peripheral zone
C. Transitional zone
D. Periurethral zone
203. Cystitis glandularis is associated with (Single best answer):
A. Pelvic lipomatosis
B. Retroperitoneal fibrosis
C. Lymphoma
204. Captopril works via:
A. Block of angiotensin I to angiotensin II
B. Block of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
205-207. True/False - Regarding AIDS nephropathy:
205. Kidneys are usually small and echogenic
206. It may be the first presentation of AIDS
207. Cannot be distinguished from end-stage renal disease of any cause
208-211. True/False - Regarding duplicated collecting systems:
208. More common in males than females
209. Ureter with ureterocele has superior and lateral insertion
210. Lower pole ureter usually obstructs
211. Only the ureter with the ureterocele obstructs
212. Most common cause of bilateral deviation of the ureters above pelvic inlet (Single best answer):
A. Lymphoma
B. Aortic aneurysm
C. Retroperitoneal fibrosis
D. Retroperitoneal sarcoma
E. Retroperitoneal hematoma
213. Regarding acquired renal cystic disease (Single best answer):
A. Cysts rarely less than 0.5 cm
B. Gets worse the longer the patient is on dialysis
214. Which testicular tumor is not germ cell origin?
A. Leydig cell tumor
B. Seminoma
C. Embryonal cell carcinoma
D. Choriocarcinoma
E. Teratoma
215-217. True/False - 32-year-old male with swollen testicle and hypoechoic intratesticular mass:
215. The location favors malignancy
216. Elevated HCG and AFP suggest extratesticular metastases
217. Would be expected to spread first to external iliac nodes
218. Most common complication of horseshoe kidney (Single best answer):
A. Stones
B. Renal hypertension
C. Infarction
220-221. True/False - Uric acid stones:
220. Associated with acidic urine
221. More common in primary gout (vs. secondary gout)
223-229. Matching:
223. Infundibular stenosis A. Reflux nephropathy
224. Polar cortical thinning B. Congenital megacalicosis
225 Amputated calyx C. Tuberculosis
226. Polygonal faceted calices D. Cortical nephrocalcinosis
E. Renal papillary necrosis
227. The location of Cowper's glands (Single best answer):
A. Into the membranous urethra
B. Into the bulbous urethra
C. Into the penile urethra
D. Into the prostate urethra
E. Into the bladder at the trigone
228-233. True/False - This scenario is likely to lead to open surgical treatment of the patient's stone.
228. Intractable urinary tract infection
229. Progressive renal damage
230. Urinary obstruction
231. Persistent pain
232. Uric acid stones
233. Struvite stones
234. Which of the following statements is part of the Meyer-Weigert rule?
A. The upper pole moiety is typically smaller
B. The upper pole moiety is more likely to become obstructed
C. The ureter from the upper moiety will enter the bladder inferiorly and medially to the ureter from the lower pole moiety
D. The lower pole ureter is more subject to reflux
235. An 8-year-old girl comes in with acute flank pain, febrile, and white blood cells in her urine. Which study should you do next?
A. Ultrasound
B. CT scan
C. MRI scan
D. VCUG
E. IVP
236. True/False - Hyperosmolar contrast causes endothelial damage.
237-241. True/False - Regarding lymphogranuloma venereum:
237. Usually asymptomatic
238. Can be treated with antibiotics
239. Associated with fistula formation
240. Associated with a retrovirus
241. More common in males than females
242. Mullerian duct is the precursor to (Single best answer):
A. Uterus
B. Seminal vesicle
C. Prostatic utricle
D. Urethra
E. Ejaculatory duct
243. A patient is given Captopril. Which of the following is expected to occur?
A. Angiotensinogen will cease to be converted to angiotensin I
B. Intraglomerular capillary hydraulic pressure will increase
C. GFR will increase
D. Tubules, under the influence of increased aldosterone, will retain more sodium
E. Efferent postglomerular arterioles will dilate
244. A patient presents with a cystine stone. Which of the following is included in an appropriate treatment regimen?
A. Hydrate to maintain urine output of 3-4 liters per day
B. Acidify the urine
C. Increase the daily intake of methionine
D. Surgical removal of the stone
245. A patient presents with a 2.6 cm calcium oxalate stone in the upper collecting system. Which is the most appropriate course of action?
A. Hydrate and wait for it to pass
B. Partial nephrectomy to include the calyx containing the stone
C. Percutaneous removal of the stone
D. Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy
246-250. True/False. A patient presents with a staghorn struvite calculus. The following could be used in an appropriate workup and treatment plan:
246. Cystogram
247. IVP with nephrotomograms
248. Medical therapy with antibiotics, no surgery
249. Surgical removal of the stone
250. ESWL
251. What KVP is used for screening mammography? (Single best answer):
A. 19-23
B. 24-28
C. 28-32
D. 33-38
E. 39-44
252. How often should phantom imaging (quality control) be done in mammography?
A. Daily
B. Weekly
C. Monthly
D. Quarterly
E. Annually
F. Semi-annually
253. What is the most likely mammographic presentation of lobular carcinoma? (Single best answer):
A. Spiculated mass
B. Calcifications
C. Architectural distortion
D. Asymmetric opacity
E. Well circumscribed mass
F. Microcalcifications
254-257. Match:
A. TP
B. TN
C. TP
254. Accuracy TN + FN TP + FN TP + FP
255. Sensitivity
256. Specificity D. TN E. TN + TP
257. Positive predictive value TN + FP TP + TN + FP + FN
258. A core biopsy is taken stereotactically from a 2-cm spiculated mass. The pathology report comes back fibroadenoma. What is the most appropriate recommendation?
A. Follow-up mammography in six months
B. Excisional biopsy of the mass
C. Follow-up mammography in one year
D. Repeat the core biopsy
E. Routine follow-up mammography
F. MRI of the breast
259-264. True/False - The following process occurs in the ductal lobular unit:
259. Nonsclerosing adenosis
260. DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ)
261. Papilloma
262. Atypical ductal hyperplasia
263. Fibrocystic changes
264. Lobular carcinoma
265. Which of the following best describes the correct needle position just prior to the firing of a biopsy gun in a breast biopsy?
C. Place the tip of the needle/core device at the periphery of, but not into the lesion. The theory is that actively growing/spreading tumor should be more peripheral.
266. A woman presents with bilateral patchy densities in the breasts and cardiomegaly. Which of the following conditions is most plausible? (Single best answer):
A. Congestive heart failure
B. Lymphoma
C. Adenocarcinoma of the breast
D. Intraductal papilloma
E. Ductal carcinoma in situ
267. A patient presents with an irregular cyst which, when biopsied, yields a malignant result. Which of the following cell types is the most likely? (Single best answer):
A. Tubular
B. Ductal
C. Medullary
D. Papillary
E. Colloid
F. Fibrocystic
268. Which of the following is the most benign form of breast cancer? (Single best answer):
A. Ductal
B. Medullary
C. Lobular
D. Papillary
E. Tubular
269. Which of the following types of breast cancer is most likely to present with a well-defined lesion? (Single best answer):
A. Ductal
B. Medullary
C. Lobular
D. Inflammatory
E. Tubular
270-274. True/False - The following are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer:
270. Apocrine metaplasia
271. Atypical ductal hyperplasia
272. Nonsclerosing adenosis
273. Sclerosing adenosis
274. Duct ectasia
275. The most common mammographic presentation of lobular cancer is (Single best answer):
A. Well circumscribed mass
B. Microcalcifications
C. Asymptomatic density
D. Architectural distortion
E. Spiculated mass
276-279. True/False - Reduction mammoplasty is associated with:
276. Elevation of nipple
277. Inferior displacement of glandular tissue
278. Skin thickening
279. Dystrophic calcification
280-283. True/False - The most common presentation of invasive lobular carcinoma is:
280. Micro Ca2+
281. Spiculated mass
282. Well defined mass
283. Architectural distortion
284. Path results of a core biopsy of a 2 cm spiculated breast mass comes back atypical hyperplasia. The next appropriate step is:
A. Repeat core
B. Six-month follow-up mammo
C. Surgical lumpectomy
D. Routine re-screen in 1 year
E. Ultrasound
285. Which subtype of ductal carcinoma in-situ has the worst prognosis?
A. Comedo
B. Cribriform
C. Micropapillary
286. What is the location within the breast of a fibroadenoma, carcinoma, and a papilloma? Know whether these lesions are within major ducts vs. the TDLU vs. the SNI, etc.
287. Know the appearance of medullary carcinoma of the breast.
288. Know what the premalignant conditions are for breast carcinoma. Know how high a risk each of those conditions is (i.e. 1.5 - 2 times the risk; 3 - 4 times the risk, etc.).
289. Scaphoid wrist fracture is most often associated with:
A. Lunate dislocation
B. Perilunate dislocation
C. Capitate fracture
D. Hamate fracture
E. Radial head fracture
290. Which tendon runs underneath the sustentaculum tali?
A. Posterior tibial
B. Flexor hallucus longus
C. Flexor digitorum longus
D. Peroneal brevis
E. Peroneal longus
291-297. Match the age with the appropriate disease:
291. 8 years A. Legg Calve Perthes
292. 12 years B. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
293. 4 years C. Transient toxic synovitis
294. 4 months D. Caffey disease
295. Newborn
296. 1 year
297. Neonatal
298. A mass in the suprascapular notch would most likely cause:
A. Infraspinatus muscle atrophy
B. Sprengel's deformity
C. Supraspinatus atrophy
D. Rhomboid muscle atrophy
E. Teres minor atrophy
F. Supraspinatus spasm
299. What runs through the median canal? (Single best answer):
A. Flexor pollucus longus tendon
B. Palmaris longus tendon
C. Ulnar nerve
D. Flexor carpi radialis tendon
E. Extensor carpi radialis tendon
300. In a patient with a SLAC lesion of the wrist, what other abnormalities should be tested for?
A. CPPD
B. HADD
C. Gout
D. TFC tear
E. Increased scapholunate distance
301. Following reduction of a posterior elbow dislocation in an adult, a free fragment is most likely from:
A. Medial epicondyle
B. Coronoid process
C. Radial head
D. Olecranon process
E. Lateral epicondyle
302. An adult pitcher with medial elbow pain. (Single best answer):
A. Radial head fracture
B. Ulnar nerve entrapment
C. Biceps tendinitis
D. Medial epicondyle fracture
E. Olecranon fracture
F. Medial epicondylitis
303. Volkmann's contracture is most closely associated with:
A. Supracondylar fracture
B. Rotator cuff injury
C. Bone fractures
D. Radial head fracture
E. Posterior elbow dislocation
304. Most common tendon to be injured in the foot:
A. Posterior tibial
B. Flexor hallucus longus
C. Flexor digitorum longus
D. ...
E. ...
Answer: A.
Reference: Berquist, MRI Musculoskeletal System, Third Edition, pages 467-483.
305. 45-year-old male playing basketball has sudden onset of severe foot pain. Most likely cause:
A. Posterior tibial tendon rupture
B. Achilles tendon rupture
C. Deltoid ligament rupture
D. Flexor digitorum longus rupture
Answer: B.
Reference: Greenspan, Orthopedic Radiology, 1997, page 9.29.
306-308. Match:
306. Myositis ossificans A. Calcifies from outside in
307. Periosteal osteosarcoma B. Mature bone centrally
308. Central osteosarcoma C. Medullary band destruction
Answers:
306. A.
307. B.
308. C.
"Myositis ossificans is characterized by immature bone centrally and mature ossification peripherally."
Reference: Greenspan, Orthopedic Radiology, 1997, pages 18.8-18.10.
309. Best sign of loosening of a non-cemented total hip arthroplasty:
A. Sclerosis around the femoral shaft tip
B. Absorption of bone adjacent to the medial femoral neck
C. Periosteal reaction adjacent to the lateral femoral shaft
D. Lateral migration of the femoral shaft
E. ...
Answer: D.
Reference: Primer of Diagnostic Imaging, page 221.
310-313. Match:
310. CPPD A. Involves the second and third digits of the hand
311. Amyloid B. Osteoarthritis of unusual joints
312. PVNS C. Marked swelling about multiple joints
313. Synovial chondromatosis D. Hemosiderin in synovium
Answers:
310. B.
311. C.
312. D.
313. C.
References: Brower, Arthritis in Black and White, 1997, pages 343-358; Greenspan, Orthopedic Radiology, 1997, pages 14.13-14.14, 15.35-15.37.
314-318. True/False - Concerning congenital dysplasia of the hip:
314. More common in males than females
315. After treatment with spica cast, an AP radiograph with straight leg is best to evaluate
316. Labrum is more echogenic than femoral head
317. Delayed ossification of femoral head occurs
318. Acetabular angle greater than 30 indicates good covering of the femoral head
Answers:
314. False. Female:Male = 8:1.
315. Probably true.
316. True.
317. True. Delayed ossification is sign of CDH.
318. False. Normal angle <30.
References: Greenspan, Orthopedic Radiology, 1997, pages 27.3-27.10; Kirks et al., Practical Pediatric Imaging, 1997, pages 465-472.
| Following answers provided by Kevin Lobo, M.D. |
319-322. True/False - Tibial plateau fracture is associated with:
319. Anterior compartment syndrome
320. Peroneal nerve injury
321. Nonunion
322. Ganglion cyst formation
Answers:
319. True. Increased pressure in compartment bounded by tibia, fascia, and interosseous membrane.
320. True.
Reference: Resnick, page 780.
321. True. Nonunion is rare after low energy plateau injuries but can be seen with severe comminution, unstable fixation, failure of bone graft, or infection.
322. True (?). Could not find a reference. However, plateau fractures are associated with ligament/meniscal injury which is associated with ganglion.
There are different classifications:
Müller - 4 types
Reference: Primer, page 370.
Schatzker - 6 types
Reference: Dahnert, page 61.
Lateral plateau fractures (80%) are most common. Medial fractures (10%) are associated with greater force and higher incidence of associated injuries. Both plateaus (10%).
Extent of fracture may be underestimated by plain films; can use tomograms or CT.
Complications:
- Malunion (common)
- 2 DJD (common)
- Ligament/meniscal injury
- Peroneal nerve injury
- Popliteal artery rupture
References: 1) Resnick; 2) Fractures in Adults, Rockwood C, Volume II, pages 1919-1954.
323-325. True/False - Regarding the axis vertebral body:
323. High (Type II) fractures are associated with nonunion
324. Hangman's fracture often decompresses the spinal canal
325. Low (Type III) fractures are unstable
Answers:
323. True. Nonunion occurs in two-thirds of high dens fractures and 100% if >5 mm of displacement. Ununified fracture called os odontoideum and indicates atlantoaxial instability.
Reference: Harris, page 441.
324. Hangman's fracture usually not associated with neurologic deficit because of small cord/canal ratio (1:3) and because of "auto-decompression" of canal.
Reference: Harris, page 379.
Effendi classification: Type I - minimal displacement; Type II - displaced with abnormal disc; Type III - displaced, C2 body is flexed, bilateral C2-3 facet dislocation.
325. True. Low dens fractures are unstable because the dens, atlas, and occiput can move as a unit separate from the axis.
Reference: Harris, page 443.
Reference: Radiology of Acute Cervical Spine Trauma, Third Edition, Harris J.
326. Which of the following fractures is most likely to cause neurologic injury (Single best answer)?
A. Hangman's
B. Odontoid
C. Flexion injury with a teardrop fragment
D. Extension injury with a teardrop fragment
E. Burst fracture
Answer: A. Flexion teardrop. Most devastating cervical injury compatible with life, characterized by anterior cord syndrome - complete, immediate quadriplegia with loss of pain, touch, temperature (anterior column) and retention of position, vibration (posterior column). All ligaments disrupted, completely unstable.
Reference: Harris, page 283.
Extension teardrop: Ant. inf. fragment height width, unstable in extension due to disruption of ALL, stable in flexion.
Hangman's: See question #315.
Burst fracture: Deficit ranges from transient parasthesia to permanent quadriplegia, but usually of lesser magnitude than flexion teardrop.
327. Adult pitcher with medial elbow pain. (Single best answer):
A. Radial head fracture
B. Ulnar nerve entrapment
C. Biceps tendinitis
D. Medial epicondyle fracture
E. Olecranon fracture
Answer: B. Ulnar nerve entrapment. Nerve trapped in fibro-osseus tunnel posterior to medial epicondyle between two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris. "Cubital tunnel syndrome" - MRI - increased signal and enlargement of nerve.
Reference: Andrews JR, Am J Sports Med 1995; 23(4):407-413. Review of 72 professional baseball players undergoing elbow arthroscopy or surgery. Diagnoses: Postmedial olecranon osteophyte (65%); ulnar collateral ligament injury (25%); ulnar neuritis (15%).
328. The most likely cause of death in a patient with a pelvic ring fracture:
A. Hemorrhage
B. Pulmonary embolus
C. Fat embolus
D. Sepsis
E. Genitourinary injury
Answer: A. Hemorrhage.
Reference: Poole GV, et al. Ann Surg 1991; 213(6):532-538.
236 pelvic fractures, 18 died: 1 from pelvic hemorrhage; 1 from PE; 4 from sepsis/organ failure; 1 from pulmonary injury; 6 from hemorrhage from other sites; 5 from head injury.
Note that death from pelvic hemorrhage is uncommon, although hemorrhage from all sites together was the most common cause of death.
329-332. True/False - Regarding Legg-Calve-Perthes disease and diagnostic bone scans:
329. Bone scans are less sensitive than plain films
330. A joint effusion will cause a false-positive result
331. Joint aspiration will cause a false-negative result
332. Increased activity is the earliest sign on bone scans
Answers:
329. False. Bone scan is more sensitive early-on.
Reference: Resnick.
330. False (?). Unable to find reference.
331. False (?). Unable to find reference.
332. False. Decreased activity is the earliest sign due to impairment of blood supply.
333. Order of distal humeral ossification centers (Single best answer):
A. CRITOE (find ages)
B. CIRTOE
C. RICTEO
D. CRIOTE
E. RCITEO
Answer: A. CRITOE.
Capitellum 1 year
Radial head 5 years
Internal (medial) 7 years
Trochlea 10 years
Olecranon 10 years
External (lateral) 11 years
(1-2 years earlier in females)
334. A 40-year-old with homogeneous 2 cm density in the proximal humerus with hex______ borders blending with adjacent bone. Mild increase uptake on bone scan.
A. Metastasis
B. Osteosarcoma
C. Enostosis (bone island)
D. Osteoid osteoma
E. ...
Answer: C. Enostosis (?).
Metastasis: Purely sclerotic metastasis - prostate; can also be seen in bronchial carcinoid, bladder, stomach, medulloblastoma and neuroblastoma.
Reference: Resnick.
Osteosarcoma: Usually in younger patients, but can occur in middle age, e.g., intraosseous low grade osteosarcoma, usually large metaphyseal purely sclerotic lesion; however, would expect marked increased uptake.
Reference: Resnick, page 1005.
Enostosis: Discrete margins with radiating spicules, usually normal bone scan, frequent in all age groups.
Reference: Resnick, page 1211.
Osteoid osteoma: Usually has central lucent area and intense uptake.
335. Signs of loosening of femoral prosthesis (Single best answer):
A. Sclerosis at tip of femoral comp.
B. Resorption of medial femoral neck/shaft
C. Heterotopic bone formation
D. Cement fracture
E. Cement bone 2 mm lucency involving 50% of interface
Answer: D. Cement fracture. This is definite evidence of loosening.
Heterotopic bone formation is of unknown etiology.
Medial bone resorption is likely related to stress shielding.
Choice E is evidence of possible loosening.
Reference: Resnick, chapter 20.
336. True/False - Amyloidosis causes marked thickening of the soft tissues (this was a musculoskeletal question).
Answer: True. Amyloid deposition can cause scleroderma-like skin changes, prominent skin nodules (especially at the olecranon, hands), and extensive infiltration about the shoulders resembling shoulder pads.
Reference: Resnick, page 605.
337. True/False - CPPD has a propensity for involvement of the second and third metacarpels.
Answer: True. Changes in the hand in CPPD predominate at the MCP joints with changes most frequent at the 2nd and 3rd MCP. In hemochromatosis, the 4th and 5th MCPs are involved more commonly than in CPPD.
Reference: Resnick, page 473.
338. Middle-aged patient with a round, sclerotic density in the proximal humerus which fades into the surrounding bone. Lesion measures approximately 1-2 cm. (Single best answer):
A. This lesion will be very hot on bone scan
B. This lesion will be mildly hot on bone scan
C. Lesion will not be seen on bone
D. Lesion will be photopenic
E. Patient will have a superscan
Answer: C. Same as #334; likely bone island. May show some uptake but "scintigraphy in cases of bone islands usually yields normal results."
Reference: Resnick, page 1211.
339. Know the ulnar carpal impaction syndrome.
Answer: Almost always associated with positive ulnar variance and chronic impaction of the ulnar head against the triangular fibrocartilage and the ulnar-sided carpal bones resulting in deterioration of the triangular fibrocartilage, chondromalacia of the lunate and ulnar head, and attrition of the luno-triquetral ligament. Findings include sclerosis, cysts, and osteophytes of the lunate, triquetrum, and ulnar head, and communicating defects of the TFC and disruption of the lunotriquetral interosseus ligament on arthrography. Treatment is with ulnar recession arthroplasty.
References: 1) Resnick, page 820; Radiology 1996; 201(2):495-500.
340-343. True/False - Concerning aggressive fibromatosis:
340. Commonly erodes bone
341. Is well defined
342. Is homogeneous on MR
343. 20% of aggressive fibromatosis metastasize to lung
Answers:
340. True or False? Both Resnick and Enzinger say "may cause pressure erosion or superficial cortical defects."
References: 1) Resnick; 2) Soft Tissue Tumors, F. Enzinger.
341. False. Poorly defined with invasion of fat or muscle; however, can be lobulated and well defined.
References: 1) Resnick; 2) Soft Tissue Tumors, F. Enzinger; 3) Dahnert, page 53.
342. False. Iso to muscle on T1. Variable on T2, can have mixed areas of cellularity (increased T2) and fibrosis (decreased T2).
References: 1) Resnick; 2) Soft Tissue Tumors, F. Enzinger; 3) Dahnert, page 53.
343. False. No cases of metastasis documented in the literature.
References: 1) Resnick; 2) Soft Tissue Tumors, F. Enzinger.
Note: Aggressive fibromatosis is also called extra-abdominal desmoid, extra-abdominal fibromatosis. Peak incidence is 25-35 years, F > M. Shoulder > chest > thigh > mesentery > neck.
References: 1) Resnick; 2) Soft Tissue Tumors, F. Enzinger.
344. Tarsalcoalition - What is the age of presentation?
397. The middle subtalar joint is involved A. Calcaneonavicular
B. Talocalcaneal
C. Calcaneocuboid
D. Talonavicular
Answer: Symptoms usually appear in 2nd or 3rd decade at the time of ossification of fibrous coalition. Calcaneonavicular (50%); talocalcaneal (35%); talonavicular (uncommon).
Reference: Resnick, page 1174.
345. True/False - Pes cavus is associated with tarsalcoalition.
Answer: True. Association with painful pes planus with peroneal spasm is well recognized.
Reference: Resnick, page 1174.
Neuroradiology:
346. Drawing of anterior cerebral artery circulation - asked to label:
A. Anterior choroidal artery
B. Sylvian point
C. Ophthalmic artery
D. Anterior temporal artery
E. Recurrent artery of Heubner
Answer: ICA has four segments:
Cervical - Usually no branches.
Petrous - Branches rarely seen on angio
- Caroticotympanic
- Vidian (pterygoid)
Cavernous - Meningohypophyseal trunk
- ILT
Supraclinoid - Ophthalmic
- Superior hypophyseal (usually not seen)
- Post. communicating
- Anterior choroidal
(Mnemonic OPA)
Recurrent artery of Heubner - Superior branch of the A. segment and supplies the caudate head and ant-inf internal capsule.
Anterior temporal artery - M1 segment trifurcates to anterior branch, posterior branch, and anterior temporal artery.
Sylvian point - On the AP view, the frontal and parietal branches of the MCA pass medially then laterally. The most superomedial point in their course is the Sylvian point.
347. The most common primary cerebral hemispheric tumor in children:
A. Glioma
B. Meningioma
C. Hemangioblastoma
D. Ependymoma
E. P.N.E.T.
Answer: A. Supratentorial tumors in children: Astrocytoma (37%); meningioma (3%); hemangioblastoma uncommon in children and supratentorial; ependymoma (5%); P.N.E.T. (2.5%).
Reference: Dahnert, pages 168-169.
348. Posterior fossa tumor in a child with a cystic component (Single best answer):
A. Juvenille pilocystic astrocytoma
B. Glioma
C. Medulloblastoma
D. Ependymoma
E. Hemangioblastoma
Answer: A. JPA is the most common pediatric infratentorial neoplasm (33%) and 60-80% of these will be cystic.
- Brainstem glioma (16-21%) (may be cystic = more aggressive)
- Medulloblastoma (26-31%) (10% are cystic)
- Ependymoma (6-14%) (small cystic-necrotic areas in 15-50%)
- Hemangioblastoma (uncommon)
Reference: Dahnert, Neuro Requisites.
349-355. True/False - Shear injury involves:
349. Brain stem
350. Splenium of corpus callosum
351. Subcortical white matter
352. Caudate nucleus
353. Temporal lobes
354. Gray white matter
355. Thalamus
Answers:
349. True. The dorsolateral midbrain is involved in the most severe cases of DAI.
350. True. Splenium of corpus callosum (and posterior body) are commonly affected by DAI.
351. True. Patients with the mildest form of DAI have injury in the subcortical white matter of the frontal and temporal lobes.
352. False.
353. True (See #351).
354. False. Cortex is spared.
355. False
Reference: Neuro Requisites, Brant & Helms, pages 57-60.
356. The most echogenic structure in a neonatal head ultrasound:
A. Cingulate gyrus
B. Corpus callosum
C. Caudate head
D. Vermis of cerebellum
E. Thalamus
Answer: C or D.
Caudate head - echogenic
Vermis of cerebellum
Corpus callosum - echopenic
Cingulate gyrus - Hypoechoic
Thalamus - hypoechoic
357. Right paracentral disc at L4/5. Most likely cause:
A. Right L5 radiculopathy
B. Right L4&5 radiculopathy
C. Right L4 radiculopathy
D. Bilateral L5 radiculopathy
E. ...
Answer: L4 root is unlikely to be affected unless the L4-5 herniation is lateral, both L5 roots are unlikely to be involved by a paracentral disc.
Reference: Resnick, page 370.
358. At what age will the white matter of children have an adult pattern of myelination on imaging studies?
A. 4 weeks
B. 4 months
C. 8 months
D. 12 months
E. 2 years
F. 4 years
G. 8 years
Answer: E. Adult myelination by 18 months.
References: Brant & Helms, page 196; Primer, page 455.
359. High parietal/convexity punctate bleeds in an older adult is most likely caused by:
A. Contusion
B. Amyloid
C. Infarction
D. Tumor
E. ...
Answer: B. Amyloid. Older patient with multiple punctate bleeds. Pattern of bleeds doesn't fit with infarct or tumor. Contusion usually occurs in frontal or anterior temporal lobes. Amyloid accounts for 31% of lobar bleeds in adults.
Reference: J Med Dent 1997; 44(1):11-19.
360-364. True/False - Orbital pseudotumor
360. Cannot be identified on CT
361. Associated with pseudotumor cerebri
362. Is painless
363. Treatment is radiation therapy
364. Rarely sensitive to steroids
Answers:
360. False. CT may show increased density of retro-orbital fat, thickening of sclera, enlargement of lacrimal gland, retrobulbar mass, or enlarged EOMs.
361. False.
362. False. Causes unilateral painful exophthalmos, decreased ocular motility, chemosis.
363. True or False (?). Steroids are the first line of Tx; however, radiation therapy is 77% effective in cases of steroid failure.
Reference: Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1990; 18(2):407.
364. False. Usually has rapid onset and good response to steroids; however, there is a more chronic form with fibrosis less responsive to steroids.
| Following answers provided by G. Michael Werdick, M.D. |
365. A 45-year-old patient with history of dry mouth for one year and history of enlarged, painless parotid glands. MRI shows cysts in bilateral parotid glands. (Single best answer):
A. HIV
B. Sjogren's syndrome
C. Lymphoepithelial cysts
D. Adenoid cystic carcinoma
E. Sialosis
Answer: A. Benign lymphoepithelial cysts are a feature of AIDS. Other possibilities include Warthin tumor and metastatic disease.
366. Which of the following are associated with Chiari I?
A. Myelomeningocele
B. Lückenschädel
C. Syringohydromyelia
D. Agenesis of corpus callosum
E. Beaked tectum
Answer: C. Twenty to thirty percent of Chiari I are associated with syringohydromyelia. A, D, E are seen in Chiari II. See Question #368 below for a complete list.
367. A 40-year-old woman presents with acute headache and seizures. T2 MRI shows increased signal in the medial temporal lobe and cingulate gyrus with no enhancement (Single best answer):
A. Infarct
B. Low grade glioma
C. Herpes encephalitis
D. Multiple sclerosis
E. HIV encephalitis
Answer: C. Herpes simplex is the most common cause of fatal endemic encephalitis. Asymmetric involvement of the temporal lobes, cingulate gyrus, insula, orbitofrontal regions are characteristic. Gliomatosis cerebri is diffuse infiltration of tumor seen as high T2 of a hemisphere with relatively little mass effect.
368-373. Matching - Diagram of an AP projection of an ICA injection:
368. Recurrent artery of Heubner
369. Anterior choroidal artery
370. Medial temporal artery
371. Sylvial point
372. Ophthalmic artery
373. Anterior temporal artery
See following diagrams for a complete list:
374. Normal adult myelination pattern is reached at what age? (Single best answer):
A. 4 months
B. 8 months
C. 1 year
D. 2 years
E. 5 years
Answer: "Myelination begins in the fifth fetal month and continues throughout life, being nearly complete at age 2 years." - Anne Osborne.
375. Young woman with worst headache of life and intrasellar/suprasellar mass with fluid/fluid level in it - Most likely lesion is (Single best answer):
A. Aneurysm
B. Pituitary adenoma
C. Craniopharyngioma
D. Meningioma
E. Rathke's cyst
Answer: History is typical for leaking aneurysm. Fluid/fluid level may be due to intramural thrombus.
376. Patient presents with an infrahyoid mass beneath the strap muscles (Single best answer):
A. Thyroglossal duct cyst
B. Brachial cleft cyst
C. Cystic hygroma
D. Glomus tumor
E. Adenopathy
Answer: A. Thyroglossal duct cysts are midline neck masses. Sixty-five percent are below the hyoid, 25% at the hyoid. Brachial cleft cysts are typically masses anterior to the sternocleidomastoid, fluid filled, but may become secondarily infected or drain to the skin. Cystic hygromas are congenital lymphangiomas, seen in utero or < 1 year, associated with Turner's. Glomus tumors are from paraganglion cells of the carotid body, very vascular and lateral in the neck.
377. Know all the differences between Chiari I and Chiari II.
Answer:
Chiari I Chiari II
Tonsils below for. magnum Tonsils below for. magnum
Normal brain stem location Beaking tectum
Syrinx in 20-75% Towering cerebellum
Associated with Klippel-Feil Scalloped petrous bone
Associated with C1, C2 Myelomeningocele
Abnormalities
IV vent compression
Small post fossa
Hydrocephalus
Agenesis of corpus callosum
Enlarged massa intermedia
Interdigitating gyri
Enlarged for. magnum
Bat-wing ventricles
Lückenschädel
378. True/False - Carotid dissection requires immediate surgery.
Answer: False. Some may be managed nonoperatively.
379. True/False - Carotid dissection is most commonly caused by penetrating trauma.
Answer: False. Blunt.
380. Patient with punctate parasagittal hemorrhages on CT scan. (Single best answer):
A. Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis
B. Transverse sinus thrombosis
C. Shear injury
D. Epidural hematoma
E. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Answer: A. Cortical and subcortical hemorrhages can sometimes be seen adjacent to the occluded sinus.
381. True/False - Chiari I patient has a large head size.
Answer: False. They are often asymptomatic.
382. True/False - Chiari II patient has a large head size.
Answer: False, although lacunar skull and small posterior fossa are characteristic.
383. UVA questions regarding a focal 1.5 cm four lateral disc at L4-5. Which nerve root is affected?
A. L4
B. L5
C. L4 & 5
D. ...
E. ...
Answer: In the lumbar region, central disk herniation compresses the root below; lateral disk herniation compresses the root above.
384-387. True/False - Concerning carotid dissections in the neck.
384. Angiography demonstrates both the false and true lumens typically
385. May present with ocular symptoms and headache
386. May present with the Horner syndrome
387. May present with pupillary dilatation
Answers:
384. False. Angiography demonstrates both the false and true lumens typically (29%).
385. True. May present with ocular symptoms and headache.
386. True. May present with the Horner syndrome
387. False. May present with pupillary dilatation.
388-389. Match disseminated necrotizing leukoencephalopathy, PML, and rubella with rapid correction of sodium, measles vaccine, treatment with intrathecal chemotherapy and radiation therapy to the brain, and immunocompromised state.
388. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
389. Central pontine myelinolysis
Answers:
Disseminated necrotizing leukoencephalopathy
Treatment with intrathecal chemotherapy
PML Immunocompromised state
Rubella
Measles Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
Central pontine myelinolysis Rapid correction of sodium
390. Adult patient with unilateral papilloma and calcification in posterior globe:
A. Drusen
B. Choroidal angioma
C. Retinoblastoma
D. Uveal melanoma
E. Phthisis bulbi
Answer: Correct answer: A.
(B: Noncalcified, most common adult benign globe tumor.)
(E: Small, contracted globe.)
391-393. Matching - Regarding tendons of the foot:
391. Tibialis post A. Most common for rupture
392. Flexor halluces longus B. Passes under sustentaculum tali
393. Flexor digitorum longus C. Inserts on navicular
Answers:
391. A.
392. B.
393. C.
394-396. Match:
394. Arthritis A. Sprue
395. Lymphoma B. Mastoiditis
396. Sclerotic bones C. Whipple's
Answers:
394. C.
395. A (Seen in 8% of sprue).
396. B.
Differential for dense bones: Renal osteodystrophy, sickle cell, myelofibrosis, osteopetrosis, pyknodysostosis, mets, mastocytosis, Paget's, athletes, fluorosis.
Reference: Helms, page 958.
Nuclear Medicine:
397-399. Which of the following would result in decreased LVEF in a MUGA?
397. Underestimate background
398. Underestimate ESV
399. Include RA in EbV
Answers:
397. Falsely low.
398. Falsely high.
399. Falsely high.
Remember the equation EF = EDV - ESV/EDV - Background. The background is subtracted in the numerator.
400-402. True/False - Regarding lung perfusion scans:
400. Minimum of 200,000 particles are needed for a diagnostic study
401. A defect may be secondary to lung cancer
402. Delivers 5 rads to the lungs
Answers:
400. False. 60,000 - 40,000.
401. True. Defect may be secondary to lung cancer.
402. False. < 1 rad.
403. A 35-year-old female with paroxysmal hypertension, history of thyroid surgery. The best initial imaging study:
A. MIBA
B. Oncoscint
C. I131
D. Gallium
E. Octreotide
Answer: A. This patient has MEN II with pheochromocytoma, medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, and hyperparathyroidism. MIBG is the agent for pheo.
404. During a dipyridamole stress study of the heart, a patient has severe angina. You should:
A. Continue the exam
B. Stop the study, give the patient nitroglycerine
C. Stop the study, give the patient aminophylline
D. Stop the study, give the patient adenosine
E. Continue the study, but give the patient nitroglycerine
Answer: C. Aminophylline will reverse the effects of dipyamidole.
405. Gallium negative study in a 35-year-old male AIDS patient who has bilateral, patchy infiltrates on chest x-ray. Most likely etiology:
A. PCP
B. MAI
C. Kaposi's sarcoma
D. Bronchogenic carcinoma
E. ...
Answer: C. Ga is avid for nearly all inflammatory conditions including PCP and sarcoid.
406. One hour after a HIDA study, bowel is visualized. Next step is (Single best answer):
A. Give glucagon
B. Give cholecystokinin
C. Stop exam
D. Give morphine
E. Have patient eat a fatty meal
Answer: D. Morphine will increase sphincter of Oddi pressure and may indicate chronic cholecystitis if gallbladder fills late.
407. A 40-year-old female with tachycardia, sweating and hypertension. What is the most appropriate next study?
A. MIBG
B. Octreotide
C. Sestamibi
D. Gallium
E. Indium
Answer: A. Imaging agent for pheo.
408. On SPECT, patient with Alzheimer's will have the following pattern:
A. Increased uptake in temporal lobes
B. Decreased uptake in parietal lobes
C. Decreased uptake in occipital lobes
A. Increased occipital uptake
C. Increased parietal and temporal uptake
D. Decreased parietal and temporal uptake
E. Increased frontal uptake
Answer: D. Seen in 80% of cases. May also be seen in Parkinson's. Increased frontal uptake is seen in Pick's disease.
| Following answers provided by Jeffrey Kuo, M.D. |
409. Best nuclear medicine test for pheochromocytoma:
A. Tc-99m sestamibi
B. I-131 MIBG
C. In-III octreotide
D. I-123 MIBG
E. Tc-99m pertechnetate
Answer: B or C. Sensitivities for I-131 MIBG and In-111 octreotide are approximately equal (88% and 96% respectively). In-111 octreotide is a more convenient agent. With I-131 MIBG, need to pretreat patient with Lugol's solution or potassium iodide.
410. Mechanism of clearance of DTPA during a VQ scan (Single best answer):
A. Alveolar capillary clearance
B. Renal excretion
C. Biliary excretion
D. Mucociliary clearance
E. Lacrimal drainage
Answer: A, if they mean clearance from the lungs; B if they mean clearance from the body. DTPA aerosol particles cross alveolar-capillary membrane with half-life of one hour; enter the pulmonary circulation and from there are rapidly cleared by the kidneys.
Reference: Mettler, Nuclear Medicine Imaging, page 144.
411. Concerning radionuclide ventriculography - Know the equation for determining ejection fraction and whether increasing or decreasing background increases or decreases the ejection fraction.
Answer: EF = End diastolic counts - end systolic counts
End diastolic counts - background counts
Increase BG causes increase ejection fraction. Decrease BG causes decrease ejection fraction.
Reference: Mettler, Nuclear Medicine Imaging, page 128.
412. True/False - The ejection fraction increases when the left atrium and left ventricle overlap.
Answer: False. Inaccurate definition of aortic or mitral valve planes with resultant inclusion of portions of either ascending aorta or left atrium in the left ventricular region of interest leads to underestimation of left ventricular ejection fraction.
Reference: Mettler, Nuclear Medicine Imaging, page 128.
413. Gallium scan in patient with AIDS is positive. What disease can be excluded?
A. Kaposi's
B. PCP
C. CMV
D. Lymphoma
E. TB
Answer: A. The lack of uptake of gallium in Kaposi's sarcoma may make gallium 67 imaging useful in differentiating between infection and sarcoma in these patients.
Reference: Mettler, Nuclear Medicine Imaging, page 260.
414. Sulfa colloid scan with hot spot least likely:
A. FNH
B. SVC obstruction
C. Budd-Chiari
D. Regenerating nodule with cirrhosis
E. Adenoma
Answer: E. Focal areas of increased uptake can result from 1) increased flow to an area, resulting in more radiocolloid delivered to normally functioning Kupffer cells or; 2) normal flow to an area of increased density of Kupffer cells. FNH has increased uptake from both vascular nature of the tumor and an increased density of functioning Kupffer cells. SVC obstruction causes increased radionuclide delivery to the quadrate lobe. Budd-Chiari causes a relative increase in uptake in the caudate than the remainder of the liver. Cirrhosis causes relative decrease in uptake in more severely affected areas and regenerating nodules will appear relatively increased in uptake. Adenomas are made up almost exclusively of hepatocytes are typically seen as cold defects.
Reference: Thrall, The Requisites, Nuclear Medicine, pages 216-218.
Pediatric Radiology:
415-420. Matching:
415. Trisomy 13 A. Brachycephaly
416. Chiari II B. Scaphocephaly
417. Coronal suture closure C. Microcephaly
418. Sagittal suture synostosis D. Macrocephaly
419. Apert's syndrome E. Microcrania
420. Dandy Walker F. Macrocrania
G. Dolichocephaly
Answers:
415. C. DDX of microcephaly: Intrauterine infection, toxic agents, drugs, hypoxia, radiation, maternal phenylketonuria, premature craniosynostosis, chromosomal abnormalities, Meckel-Gruber.
Reference: Dahnert, page 226.
416. G. Enlargement of occipital homs and atria due to maldeveloped occipital lobes.
Reference: Dahnert, page 199.
417. A. Coronal synostosis is the second-most common type and results in plagiocephaly when unilateral ("harlequin eye") and brachycephaly when bilateral.
418. B. Sagittal suture craniosynostosis is the most common type and results in dolichocephaly = scaphocephaly = elongation of the skull in the AP dimension.
419. C and E. Apert syndrome is AD. Oxycephalic skull (premature closure of sagittal, coronal, and lambdoid sutures), hypoplasia sinuses, fusion of phalanges, metacarpals, carpals, absence middle phalanges.
420. B and D. Large skull secondary to hydrocephalus and dolichocephaly.
Reference: Dahnert, page 203.
421. Five-day-old full-term baby underwent cardiac angiography for evaluation of VSD and coarctation of the aorta. Two to three days later, an x-ray showed dilated bowel with pneumatosis. Most appropriate action:
A. Repeat the film in 24-48 hours
B. Barium enema to find perforation
C. Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan
D. Decubitus film to look for free air
E. Aortic ultrasound to detect thrombosis
F. Cross-table lateral to rule out free air
Answer: D. The major concern is for ischemic bowel/necrotizing enterocolitis. The only true radiograph indication for surgery is perforation. If a perforation is suspected, a left lateral decubitus film is preferred over the supine cross-table lateral exam. Barium is contraindicated. Remember that gas in the portal system does not imply a bad outcome as is does in the adult.
Reference: Blickman, Pediatric Radiology, The Requisites, page 63-65.
422. The most common type of tracheo-esophageal abnormality:
A. Distal fistula with esophageal atresia
B. Proximal and distal fistulas
C. H-type fistula
D. Proximal and distal atresia without fistula
E. Distal atresia and proximal fistula
Answer: B. Most common is EA and distal fistula (82%), then EA without fistula (9%), no EA with H-type fistula (6%), EA and two fistulas (2%), proximal fistula and distal EA (1%).
Reference: Blickman, Pediatric Radiology, The Requisites, page 71.
423. The lowest level of the tip of the conus in the normal neonate:
A. T10-11
B. T12
C. L2
D. L422 E. S1
Answer: C. Tethering of the cord id caused by primary shortening of the filum terminale or is secondary to dysraphic changes preventing the normal "ascent" of the conus medullaris above L2-3. In an infant, US may demonstrate low termination of the conus below L2 or L2-3.
Reference: Blickman, Pediatric Radiology, The Requisites, page 228.
424. Two-year-old female with first UTI. Next test (Single best answer):
A. VCUG or RNC
B. Renal US
C. DMSA
D. IVP
E. Glucoheptonate
Answer: A. At Children's Healthcare Minneapolis, everyone gets a VCUG first. Some folks at Fairview argue that a RNC is okay as an initial study for a girl as it is more sensitive and has less radiation exposure. VCUG must be done in all males to look for urethral pathology (e.g., PUV).
425. A newborn presents with failure to thrive, difficulty feeding, and intermittent cyanosis. Failure to pass NG tube and normal CXR. What test would you order next?
A. Chest CT
B. Upper GI
C. BE
D. Renal ultrasound
E. Pulmonary function tests
Answer: B. The main concern is for a tracheo-esophageal abnormality. A carefully performed UGI is the study of choice.
426. Most common type of TE fistula is (Single best answer):
A. Distal fistula/proximal atresia
B. Esophageal atresia, no fistula
C. H-type fistula
D. ...
E. ...
Answer: ? (Question was not answered.)
427-430. Match:
427. Hemangioblastoma A. Sturge-Weber
428. Venous angioma B. Von Hippel-Lindau
429. Port wine stain C. Osler-Weber-Rendu
430. Telangiectasia D. Other phakomatoses
Answers:
427. B. Von Hippel-Lindau is AD (chromosome 3) consisting of retinal, cerebellar and visceral angiomatous lesion including hemangioblastomas.
428. A. See below.
429. A. Sturge-Weber is characterized by facial port wine stain in VI distribution, leptomeningeal venous angiomas, subpial tramlino calcifications.
430. C. Autosomal dominant inheritance and manifests as cutaneous and mucous membrane telangiectasias, AVM, and aneurysm.
431-433. True/False - Wilms tumor:
431. Associated with hereditary aniridia
432. Associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
433. Most common pediatric tumor to invade IVC
Answers:
431. False. Wilms tumor is associated with sporadic aniridia, hemihypertrophy, Drash syndrome, and GU anomalies.
Reference: Dahnert, page 713.
432. True. Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome = EMG syndrome = exophthalmos, macroglossia, gigantism + hepatomegaly, hyperglycemia from islet cell hyperplasia.
Reference: Dahnert, page 713.
433. True. Wilms tumor is most common abdominal neoplasm in children from 1-8 y.o. and third-most common malignancy in childhood after leukemia and brain tumors. Four to ten percent invade IVC/RA.
Reference: Dahnert, page 713.
434. True/False - Celiac sprue is associated with transient intussusception.
Answer: True. Transient nonobstructive intussusception (20%) without anatomic lead point.
Reference: Dahnert, page 626.
435. True/False - Cystic fibrosis is associated with meconium plug syndrome.
Answer: False. Meconium plug syndrome is neonatal low colonic obstruction due to colonic inertia, usually in full-term babies. It is associated with diabetic mothers and mothers treated with MgSO4 for preeclampsia.
Reference: Dahnert, page 616.
Ultrasound:
436. Expected time that corpus luteum should no longer be present (Single best answer):
A. 5 weeks of pregnancy
B. 10 weeks of pregnancy
C. 15 weeks of pregnancy
D. 20 weeks of pregnancy
E. 24 weeks of pregnancy
Answer: D. Corpus luteum of pregnancy can grow up to 15 cm. Maximum size at 8-10 weeks. Usually resolves before 20 weeks of GA.
Reference: Dahnert, page 743.
437-441. True/False - High output heart failure in utero:
437. Decrease size umbilical vein
438. Increase placental thickness
439. Polyhydramnios
440. Increased fetal movement
441. Skin thickening
Answers:
437. False. Findings in hydrops include anasarca = skin edema (skin thickness > 5 mm), ascites, pleural effusion, increased diameter of umbilical vein, polyhydramnios, placentomegaly > 6 cm, pericardial effusion, hepatosplenomegaly.
Reference: Dahnert, page 749.
438. True.
439. True.
440. False.
441. True.
442. Most common sonographic evidence of malignant thyroid lesion:
A. Poorly defined margins
B. Peripheral calcification
C. Increased Doppler flow
D. Microcalcifications
E. Hypoechogenicity
Answer: D. Thyroid cancer is typically hypoechoic and has poorly defined margins. One feature that should prompt particular concern is microcalcifications, because these are more predictive of cancer than is any other sonographic finding.
Reference: (Kurtz, Ultrasound Requisites, page 451.)
443-445. True/False - Regarding power Doppler
443. Depends on signal amplitude
444. Color indicates flow velocity
445. Provides same information as color Doppler regarding direction of blood flow
Answers:
443. True. Instead of displaying the mean Doppler frequency shift, power Doppler images display the integrated power of the Doppler signal. It is theoretically velocity and Doppler angle independent and not subject to aliasing.
Reference: Rubin, Radiology 1994; 190:853-856.
444. False.
445. False.
446-448. True/False - Re: endometrial stripe thickness:
446. EM polyps can mimic thickening
447. Best measured n coronal plane
448. Best measured in sagittal plane
Answers:
446. True. DDX of thickening: EM polyp, hyperplasia, endometriosis, endometrial carcinoma. Tamoxifen, met, mole, incomplete abortion, submucosal leiomyoma.
Reference: Dahnert, 728.
447. False.
448. True.
449-451. True/False - Concerning Tamoxifen effects on the endometrium:
449. Causes endometrial polyps
450. Antiestrogenic affect on the endometrium
451. Thin endometrium may cause bleeding when the endometrial stripe measures less than 4 mm thick
Answers:
449. True. An increased incidence of endometrial changes including hyperplasia, polyps, and endometrial cancer has been reported with Tamoxifen likely secondary to partial estrogenic properties.
Reference: PDR.
450. False.
451. False. The statement is true in that endometrial atrophy can result in uterine bleeding, but Tamoxifen results in more proliferative changes on endometrium.
452. When does the corpus luteum of pregnancy disappear?
A. 5 weeks
B. 10 weeks
C. 15 weeks
D. 20 weeks
E. ...