RAPHEX 2002 Questions
G 1. Which of the following is not equal to one Gray?
A. 1.0 Joule/kg.
B. l00 rads.
C. 1.0 Sv/QF
D. (100 Roentgen) (f-factor).
E. 100 ergs/gm.
G2-GS. Match the unit with the quantity it measures. (Answers may be used more than once or not at all.)
A. Frequency.
B. Wavelength.
C. Power.
D. Absorbed dose.
E. Energy.
G2. Electron volt
G3. Hertz
G4. Joule
G5. Gray
G6-G I 0. Match the elementary particle, as described by its characteristics below, to the following description. (Answers may be used more than once.)
Charge Rest Mass
A. +1 0.51MeV
B. +1 930MeV
C. +1 140MeV
D. 0 930MeV
E. -1 0.51 MeV
G6. Is the nucleus of a hydrogen atom.
G7. Is emitted during beta decay when Z decreases by 1.
G8. Is responsible for x-ray production.
G9. When this particle combines with an electron, annihilation photons are emitted.
G10. There are 2 of these in a Tritium nucleus.
G 11. Directly ionizing radiation includes all of the following except:
A. Electrons
B. Positrons
C. Alpha particles
D. Neutrons
E. Betas
G 12. Which of the following is true?
A. Elements can only have one stable isotope.
B. Elements can only have one radioactive isotope.
C. Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons.
D. Isotopes of the same element have the same number of neutrons.
E. Stable elements have equal numbers of protons and electrons.
G 13. The product of an (n, y) reaction is an _____ of the target atom.
A. Isotone
B. Isobar
C. Isotope
D. Isomer
G 14. The mass number A of an atom is the number of_____
A. Neutrons in the nucleus
B. Protons in the nucleus
C. Protons, electrons, and neutrons
D. Protons and neutrons
E. Protons and electrons
G15. 226/88Ra contains 88 ____
A. Electrons
B. Neutrons
C. Nucleons
D. Protons and neutrons
G 16. When an electron is removed from an atom, the atom is said to be
A. Radioactive
B. Ionized
C. Inert
D. Excited
E. Metastable
G I 7. Tungsten has a K-shell binding energy of 69.5 keV Which of the following is true?
A. The L-shell has a higher binding energy.
B. Carbon has a higher K-shell binding energy.
C. Two successive 35 keV photons could remove an electron from the K-shell.
D. A 69 keV photon could not remove the K-shell electron, but could remove an L-shell electron.
G 18. Inert atoms with Z greater than 2 have _____ electrons in the outer shell.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
E. n, where n is the outer shell number
G 19. A radioactive source has a half-life of 74 days, and an activity of 2.0 MBq. 37 days ago the activity was _____ MBq.
A. 4.00
B. 3.00
C. 2.83
D. 2.61
E. 2.50
G 20. A radioactive source with a half-life of 60 days will decay to _____ of its initial activity in 7 days.
A. 1.08
B. 0.98
C. 0.92
D. 0.82
E. 0.79
G21. After 5 half-lives, the fraction of activity remaining is _____
A. (l/2)5
B. (1/5)2
C. 1/10
D. 1/5
E. 1/64
G22. If the physical half-life, Tp, is much greater than the biological half-life, Tb, the effective half-life is _______
A. Close to Tp
B. Close to Tb
C. The average of Tp and Tb
D. (Tp + Tb)1(TpTb)
G23-G30. Match the mode of decay to the description below:
A. Beta minus
B. Beta plus
C. Alpha
D. Isomeric
G23. Ra-226 to Rn-222
G24. Z increases by 1
G25. Z decreases by 1
G26. Z decreases by 2
G27. A and Z remain constant
G28. Tritium (H-3) to Helium (He-3)
G29. TC-99m to Tc-99
G30. Electron capture can be a competing mode of decay to this.
G31. In which of the following types of decay are the products emitted with a continuous energy spectrum?
A. Alpha.
B. Beta.
C. Gamma.
D. Alpha and beta.
E. Alpha and gamma.
G32-G33. Match the type of radionuclide with the production method.
A. Beta plus emitter.
B. Beta minus emitter.
C. Alpha emitter.
D. A or B.
032. Separation from reactor-generated fission products.
033. Cyclotron-produced radionuclides.
G34. A naturally occurring radionuclide found in the soil has a half-life of 3 days. The total amount of this nuclide compared to the amount found 6 days earlier is about _____
A. 1/4
B. 1/2
C. The same
D. Twice as much
G35. One Ci is equal to _____ disintegrations/sec.
A. 3.7x10*7
B. 3.7 x 10*10
C. 2.7 x 10*-8
D. 2.7x10*-11
E. l.4x10*6
G36. The dose rate at 1 m from a radioactive source is closest to its source-strength measured in _____
A. mg Ra equivalent
B. Curies
C. Air kerma rate
D. GBq
G37. The exposure rate constant for a radionuclide is 12.9 Rcm*2/mCi-hr. How many HVLs of shielding are required to reduce the exposure rate from a 19.5 mCi source at 2 m to less than 2 mR/hr?
A. 1.
B. 2.
C. 3.
D. 4.
E. 6.
G38. The ratio of heat to x-rays produced in a typical diagnostic target is about _____
A. 1:99
B. 10:90
C. 50:50
D. 90:10
E. 99:1
G39. In an x-ray machine with a tungsten target, increasing the kVp from 100 to 150 will increase all of the following except:
A. The total number of x-rays emitted.
B. The maximum energy of the x-rays.
C. The average energy of the spectrum.
D. The energy of the characteristic x-rays.
E. The heat units generated (for the same mAs).
G40. Tungsten has the following binding energies: K = 69 keV, L = 12 keV, M = 2 keV. A 68 keV electron striking a tungsten target could cause emission of which of the following photons?
1. 66 keV characteristic x-ray.
2. 57 keV bremsstrahlung.
3. 57 keV characteristic x-ray.
4. 10 keV characteristic x-ray.
A. 1,2,3,4
B. 1,3
C. 2,4
D. 4 only
G41. In a typical diagnostic x-ray beam from a tungsten target, characteristic radiation amounts to _____ % of the total beam.
A. 0-20
B. 20-50
C. 50-90
D. 90-100
G42. The quality of a diagnostic x-ray beam is determined by measuring the _____
A. Peak tube voltage.
B. Effective kV of the beam.
C. Percent (%) transmission through 10 cm of water.
D. The mm of Al filtration added to the beam.
E. The half-value layer in Al.
G43. The effective photon energy of an x-ray beam can be increased by
A. Increasing the tube current.
B. Decreasing the filtration.
C. Increasing the mAs.
D. Increasing the tube voltage.
E. All of the above.
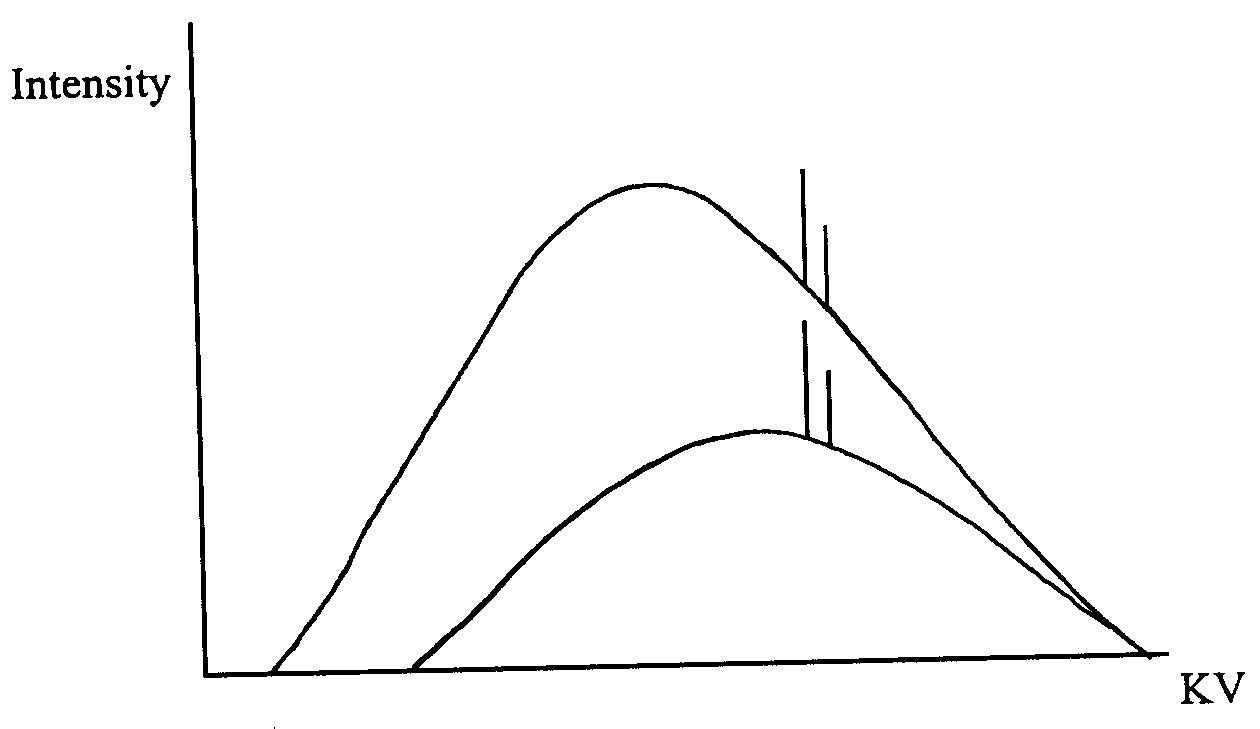
G44.
The two x-ray spectra shown have the same _____
1. Filtration
2. Target material
3. HVL
4. kVp
A. 1,2,3,4
B. 1,3
C. 2,4
D. 4 only
G45. A diagnostic x-ray beam has an HVL of 2 mmAl. If the filtration is increased by 0.5 mmAl the resulting beam will have _____ HVL and _____ intensity.
A. Greater Greater
B. Greater Less
C. Same Less
D. Less Less
E. Less Greater
G46-G50. Match the type of radiation with its description.
A. Ionizing elementary particles
B. Non-ionizing elementary particles
C. Ionizing photons
D. Non-ionizing photons
E. Other
G46. Betas
G47. Heat radiation
G48. Visible light
G49. X-rays
G50. Ultrasound
G51. Visible light has a wavelength of about 6 x l0-7 m. Co-60 gammas have a wavelength of 10-12 m and an energy of 1.2 MeV The approximate energy of visible light is _____
A. 720 MeV
B. 72 keV
C. 2eV
D. 2 x l0*-6eV
E. 7.2 x10*-4eV
G52. The output of a fluoroscopic unit is 10 mR/min at 50 cm. The output at 75 cm is _____ mR/mm.
A. 15.0
B. 7.5
C. 6.6
D. 5.0
E. 4.4
G53. The linear attenuation coefficient μ of a beam is 0.1 cm-1. The HVL is _____
A. 14.4cm
B. 6.93 cm
C. 1.44cm
D. 0.693 cm
E. 0.693 mm
G54. Two materials are irradiated by photons. Material A has an atomic number of 14 and B has an atomic number of 7. The photoelectric component of the mass attenuation coefficient of A is _____ times that of B.
A. 16
B. 8
C. 4
D. 2
E. 0.5
G55. Which of the following statements regarding photoelectric interactions is false?
A. They are mainly responsible for differential attenuation in diagnostic radiographs.
B. The incident photon is absorbed.
C. The probability increases rapidly with increasing energy.
D. Bound electrons are involved.
G56. A photon detected following a photoelectric interaction is most likely to be _____
A. The scattered incident photon
B. A gamma ray
C. An annihilation photon
D. A characteristic x-ray
E. Cerenkov radiation
G57. At x-ray energies between 40 and 100 keV _____ absorbs more energy than _____ per gram.
A. fat, muscle
B. muscle, bone
C. iodine, bone
D. fat, air
E. air, muscle
G58. In a Compton interaction, which of the following is true?
A. The scattered photon can be emitted at any angle.
B. The photon is totally absorbed.
C. A characteristic x-ray and an electron are emitted.
D. Compton electrons can be backscattered.
G59. The ratio of the number of Compton interactions in one gram of calcium to one gram of carbon is about _____
A. 2:1
B. 1:1
C. 1:2
D. It depends on the photon energy
E. In the ratio of their densities
G60. Which of the following is false? A photon can undergo a _____ interaction followed by a _____ interaction.
A. Compton, pair production
B. Compton, another Compton
C. Compton, photoelectric
D. Photoelectric, Compton
G61. In the Compton process, which of the following is true?
A. Attenuation per gram depends on the Z of the absorber.
B. The interaction is primarily with inner bound electrons.
C. It is the dominant process for photons in the 5-10 keV range interacting with tissue.
D. Attenuation per gram depends on the electron density.
G62. The energy absorbed in pair production is:
A. The incident photon energy, Ei
B. Ei-1.02MeV
C. Ei-0.51MeV
D. Ei +1.02 MeV
E. 0.51 MeV
G63. In pair production, which of the following is true?
A. The incident photon is scattered with reduced energy.
B. Annihilation photons always have an energy of 0.51 MeV each.
C. A pair of orbital electrons are ejected from the atom.
D. Two positrons are emitted at 180 degrees.
E. It cannot occur if the photon energy is above 1.02 MeV
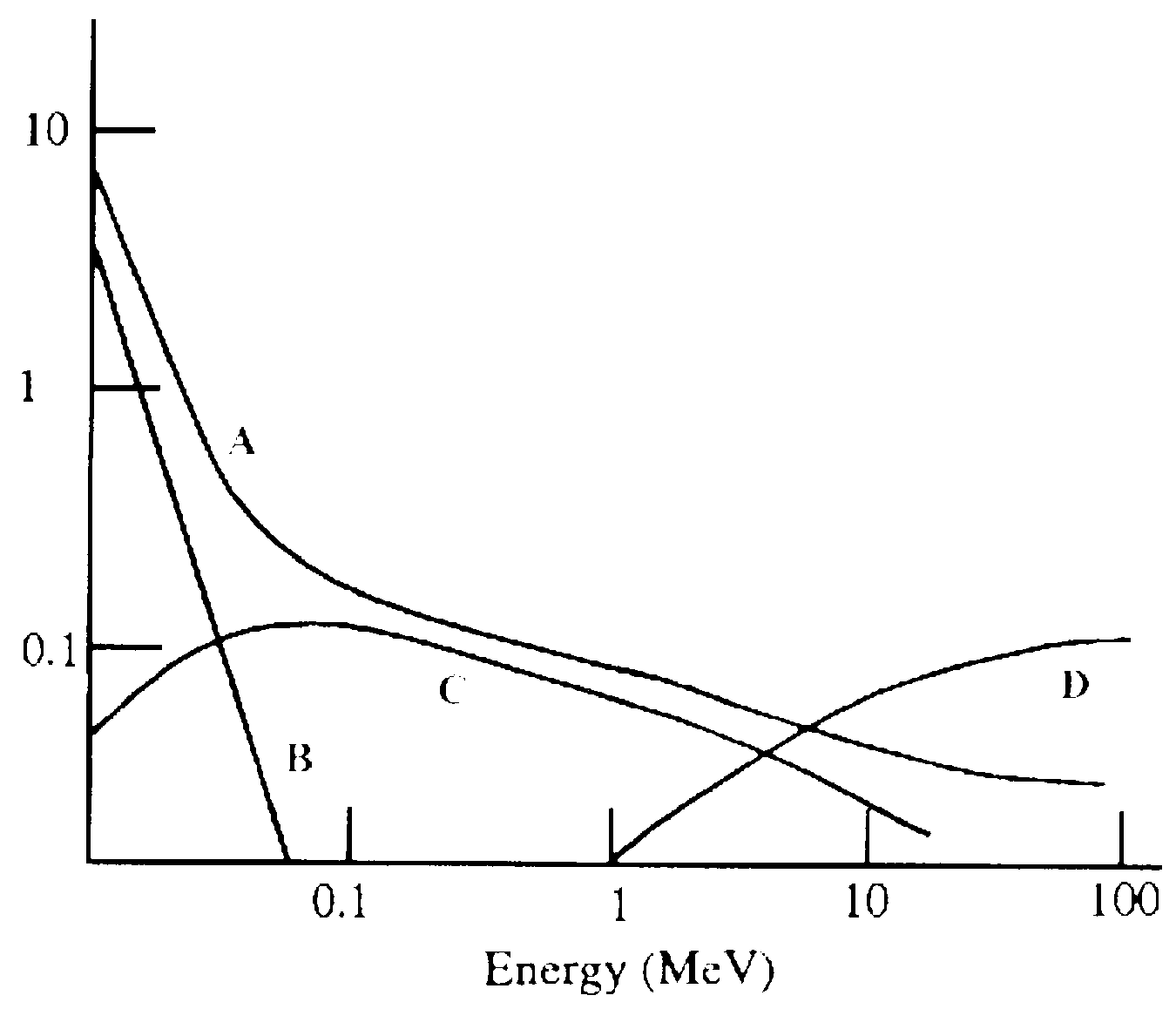
G64-G66. Match the interaction process with the appropriate mass attenuation coefficient curve.
G64. Pair production (in lead)
G65. Compton (in water)
G66. Photoelectric (in water) 1
G67-G68. Match the type of interaction mainly responsible for the effect:
A. Compton scattered photons.
B. Compton electrons.
C. Pair production.
D. Photoelectric interaction.
E. Photo-nuclear disintegration.
G67. Differential absorption in diagnostic radiographs.
G68. Loss of contrast in a lateral pelvic radiograph of a large patient.
G69. PET scan images are created by detecting:
A. Positrons emitted from the region of uptake.
B. Annihilation photons.
C. Protons emitted from the region of uptake.
D. The paths of the positrons traveling through tissue.
G70. The radiation which has the greatest range in tissue is _____
A. An 8 MeV alpha particle
B. A 2 MeV beta particle
C. A 20 keV auger electron
D. A 1 MeV positron
E. A 20 keV proton
G7 I. The absorption of a neutron can result in emission of_____
A. A photon
B. An alpha particle
C. A proton
D. Two neutrons
E. All of the above
G72. Neutrons have a higher Quality Factor than electrons because:
A. They transfer energy to protons which have a high LET.
B. They slow down in tissue, and deposit a lot of energy at the ends of their tracks.
C. They have a large mass and charge.
D. They are directly ionizing.
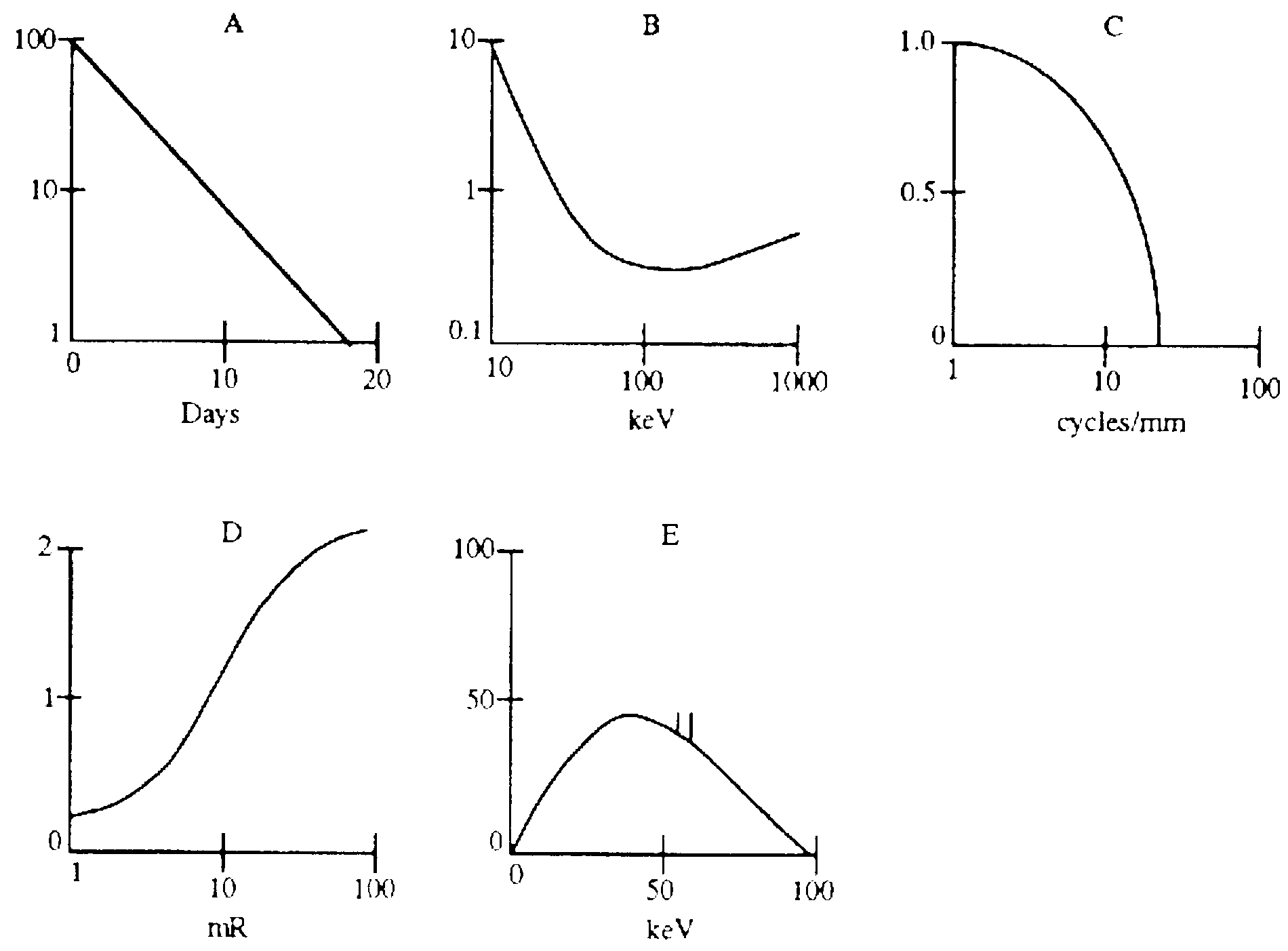
G73-G74.
073. Which graph represents the shape of an H&D (H and density) curve?
074. Which graph represents radioactive decay?
G75. A grid improves the quality of a diagnostic x-ray primarily by attenuating
A. Primary photons
B. Compton scattered photons
C. Compton electrons
D. Photoelectrons
E. Coherent scattered photons
G76. Regarding geometric unsharpness, which of the following is false? It is:
A. Inversely proportional to focal spot size.
B. Directly proportional to object-film distance.
C. Inversely proportional to focal spot-object distance.
D. Characterized by penumbra width.
G77. The purpose of a screen is to:
1. Convert x-rays to light photons.
2. Reduce scatter reaching the film.
3. Reduce patient's exposure.
4. Increase radiographic resolution.
A. 1,2,3,4
B. 2 only
C. 2,4
D. 1,3
E. 4 only
G78. A film of optical density (OD) 0.75 is placed over another identical film. The OD of the pair is _____
A. 0.75
B. 1.0
C. 1.5
D. 1.75
E. 2.25
G79. A series of measurements has a mean of 100 counts. A range of +/-1σ is _____
A. 95-105
B. 90-110
C. 68-137
D. 50-150
E. 33-167
G80. To achieve a standard deviation of 2%, _____ counts must be collected.
A. 400
B. 1,414
C. 2,500
D. 10,000
E. 40,000
G81. Information will be destroyed in/on a _____ when the computer power is turned off.
A. Floppy disk
B. Hard disk
C. Magnetic tape
D. RAM
E. ROM
G82. Concerning digital computers, all of the following are true, except:
A. ROM stands for Random Order Memory.
B. A Word is a set of consecutive bits treated as an entity, and occupying one storage location in memory.
C. A byte contains 8 bits.
D. A modem is a device that converts a digital signal into a frequency-coded signal for transmission over a telephone line.
G83-G85. Match the following prefixes with the correct power of 10:
A. 10-12
B. 10-6
C. 106
D. 109
E. 1012
G83. micro
G84. mega
G85. giga
G86. Radon represents an environmental hazard primarily in:
A. Wooden buildings.
B. High rise apartment buildings.
C. Basements and ground floor apartments.
D. The outdoors.
G87. The annual average natural background radiation dose to members of the public in the United States, excluding radon, is approximately _____ mrem.
A. 10
B. 50
C. 100
D. 200
E. 400
G88. The largest contribution to the radiation exposure of the U.S. population as a whole is from:
A. Radon in the home.
B. Medical x-rays.
C. Nuclear medicine procedures.
D. The nuclear power industry.
G89. The currently accepted model of radiation dose versus effect used by regulatory agencies to determine dose standards is _____
A. Linear quadratic.
B. Exponential.
C. Cubic.
D. Linear, threshold.
E. Linear, no threshold.
G90. A whole body dose of 5 mSv/yr for 20 years would increase a radiation worker's risk of cancer by approximately _____ %
A. 0.05
B. 0.5
C. 5
D. 10
G91. The latent period for radiation-induced solid tumors is about _____ years.
A. 1
B. 5
C. 10
D. 20
E. 50
G92. Regarding radiation effects in the embryo:
A. Prenatal death is equally likely at all stages of development.
B. Neonatal death is most likely for embryos irradiated in the last trimester.
C. Embryonic cells are resistant to radiation because of an efficient repair mechanism.
D. Most congenital abnormalities occur during the period of organogenesis.
G93. The estimated increased risk of birth defect in a fetus receiving 1 rem (10 mSv) in the 12th week of gestation is about _____
A. 0.01
B. 0.1
C. 1.0
D. 10
G94. According to NCRP Report No. 116, the recommended maximum annual dose equivalent for radiation workers' whole body is _____ mSv and for the hands is _____ mSv.
A. 5 5
B. 5 50
C. 10 100
D. 50 50
E. 50 500
G95. Film badges:
A. Can measure only the total dose of radiation, but cannot distinguish between low and high energy x-rays.
B. Can measure exposures of 1 mR.
C. Are insensitive to heat.
D. Use the optical density of the film to measure dose.
G96. 100 μSv is equal to _____ mrem.
A. 100
B. 10
C. 1
D. 0.1
E. 0.01
G97. If one lead apron attenuates 95% of an x-ray beam, two aprons will transmit approximately
A. 10
B. 5
C. 2.5
D. 1.25
E. 0.25
G98. When calculating room shielding, the use factor U refers to:
A. The weekly dose at the isocenter.
B. The fraction of operating time that the area in question is occupied.
C. The fraction of operating time that the beam is directed towards the barrier.
D. The fraction of the work week that the machine is in operation.
G99. When designing shielding for an x-ray machine, regulations require that the barrier for a fully-occupied non-controlled area must be about _____ HVLs thicker than that for a controlled area.
A. 50
B. 10
C. 6
D. 2
E. 1
G 100. After installation of a chest x-ray unit, which agency regulates its operation?
A. NRC
B. OSHA
C. HICFA
D. State
D 1. For a 70 kVp x-ray beam, the mass attenuation coefficient which varies the most from muscle tissue is:
A. Air.
B. Aluminum.
C. Bone.
D. Fat.
E. Iodine.
D2-DS. Select the interaction that predominates in the following situations:
A. Compton scattering
B. Photoelectric interaction
C. Pair production
D. None of the above
D2. 30 kVp, adipose tissue
D3. 90 kVp, muscle
D4. 90 kVp, iodine contrast
D5. 90 kVp, LaOBr intensifying screen
D6. The first half-value layer (HVL) for an 80 kVp x-ray beam is about equal to:
A. 20-40 mmAl.
B. 2-4 cm soft tissue.
C. 2-4 mm lead.
D. 2-4 cm bone.
D7. The _____ rating of an x-ray tube is based on the maximum energy input that the tube target track can sustain without damage.
A. anode heat capacity
B. cathode heat capacity
C. housing heat capacity
D. anode cooling
E. single exposure
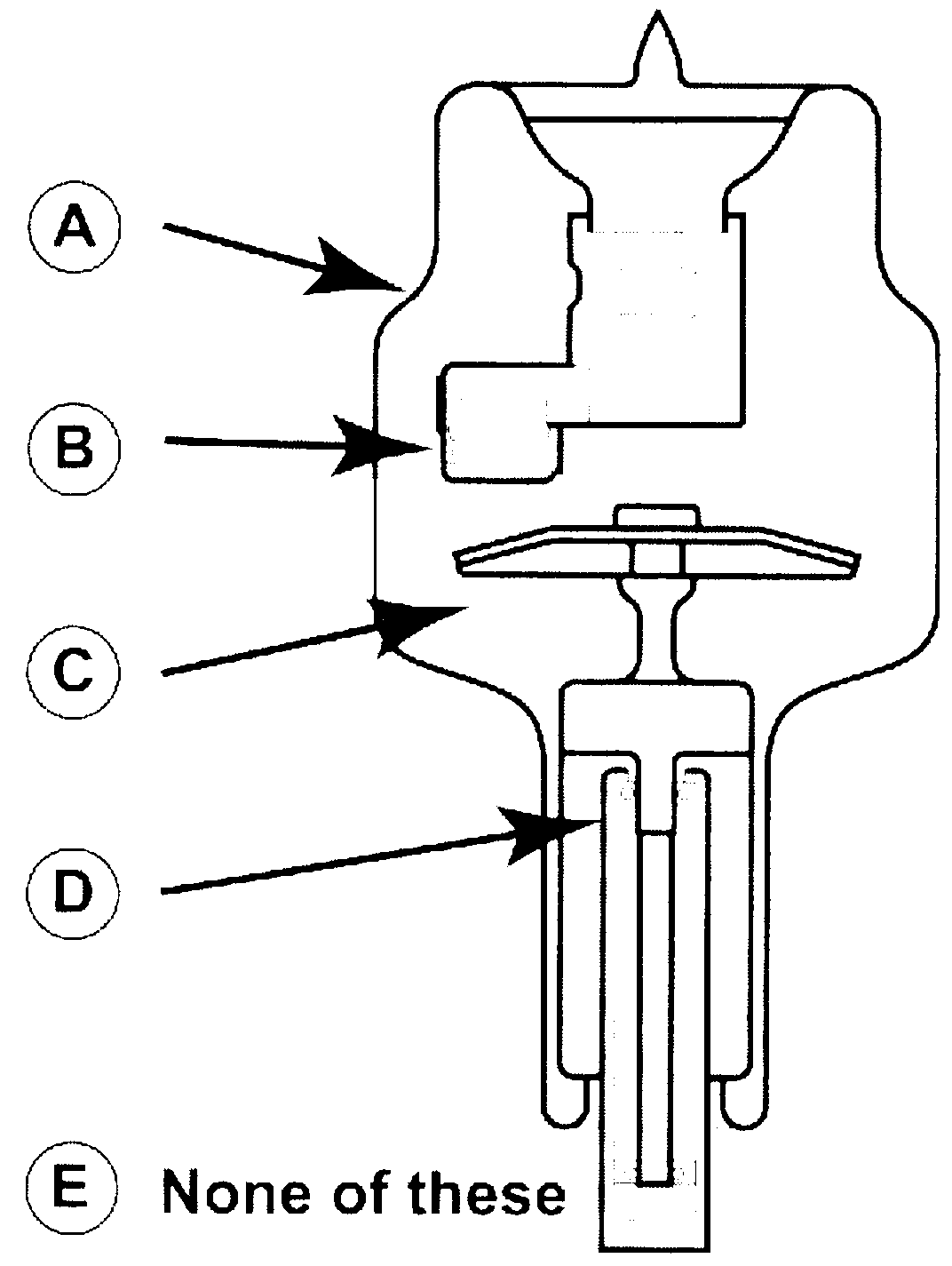
D8-D11. Match the following components to the figure of the x-ray tube:
D8. Anode ______
D9. Bearings ______
Dl0. Cathode ______
Dl1. Vacuum envelope
D 12. A newly installed bucky radiographic system produces abdominal images that are of acceptable density over the spine and progressively lighter toward both lateral edges of the film. The most likely reason for this finding is improper:
A. Collimator tracking.
B. Focal distance for grid.
C. Grid ratio.
D. kVp calibration of the system.
E. Programming of the AEC system.
D 13. The impression of noise in an x-ray image is:
A. Increased by increasing the film speed in a screen-film cassette.
B. Decreased by increasing the film speed in a screen-film cassette.
C. Increased by decreasing the focal-spot size.
D. Decreased by decreasing the focal-spot size.
E. Mainly determined by imperfections in the image receptor.
D 14. The imaging system which is best for visualizing small differences in the physical density of objects is:
A. CT.
B. Film-screen radiography.
C. II fluoroscopy.
D. MRI.
E. Ultrasound.
D 15. The penumbra associated with the image of the edge of an object placed 50 cm above the film plane, for an SID of 100 cm, and a focal spot size of 1.0 mm is ______ mm.
A. 0.01
B. 0.1
C. 1.0
D. 10
D 16. In the figure below, the factor which was changed to produce the two different x-ray spectra was the ______
A. Target material
B. Filtration
C. mAs
D. kVp
E. Anode angle
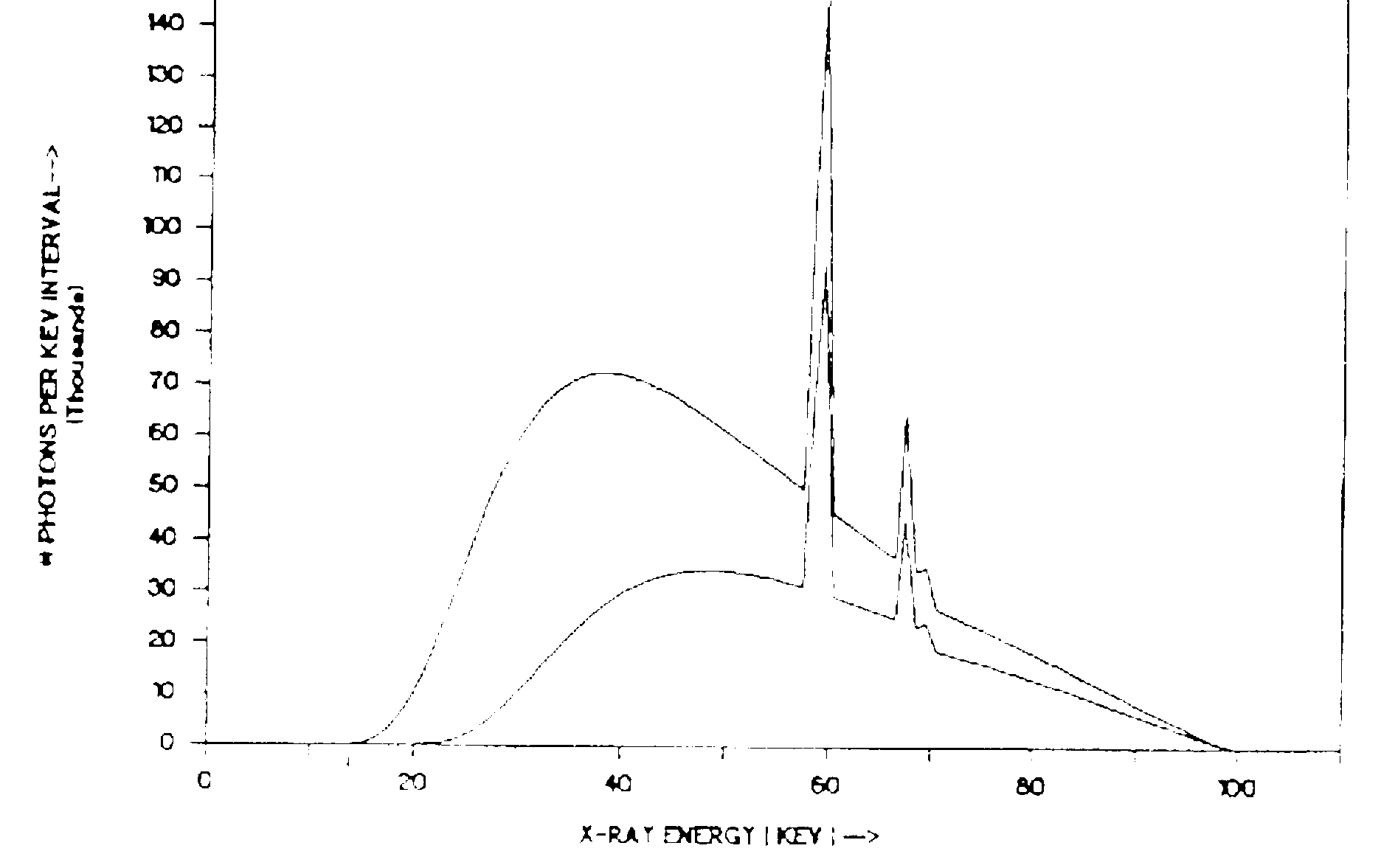
D 17. A measurement of the cardiac dimensions is obtained from a chest film. The SID is 72" and the heart is midway in a 14" chest. The distance between the chest changer surface and the film is 3". The dimensions on the film are ______ than the actual anatomy.
A. 32% larger
B. 16% larger
C. 8% smaller
D. 16% smaller
E. 32% smaller
D18. The main reason a 12:1 grid is never used with portable radiography is:
A. There will be too much grid cut-off if the grid is not positioned properly.
B. The output of portable x-ray units is too low.
C. It is necessary to keep exposure times under 10 ms.
D. The increased scatter makes for wider latitude radiographs which are undesirable for portable chest x-rays.
E. High ratio grids may only be used at high kVp. Portable x-ray units only go up to 90 kVp.
D 19. Abdominal radiographs taken at high kVp without a grid can be expected to have considerable scatter. The ratio (S/P) of scattered photons (S) to unscattered primary photons (P) reaching a screen-film combination without a grid is about ______
A. 0.2
B. 0.5
C. 1.0
D. 4.0
E. 20.0
D20. Concerning linear blurring tomography, which of the following is false?
A. It uses a conventional grid.
B. It achieves a section thickness of about 2 mm using a wide angle.
C. It requires a higher patient x-ray exposure than a plain film.
D. It requires long exposure times for thin sections.
E. It yields very high contrast images for thin sections.
D21. Failure to use adequate fixer for radiographic film processing will:
A. Decrease the film contrast gradient.
B. Decrease film speed.
C. Increase quantum mottle.
D. Increase silver reclamation.
E. Decrease archival storage.
D22. Low specific gravity of the developer solution (dilution of the chemistry) for film processing will:
A. Increase film contrast gradient.
B. Increase "base + fog".
C. Decrease film speed.
D. Decrease archival storage.
E. All of the above.
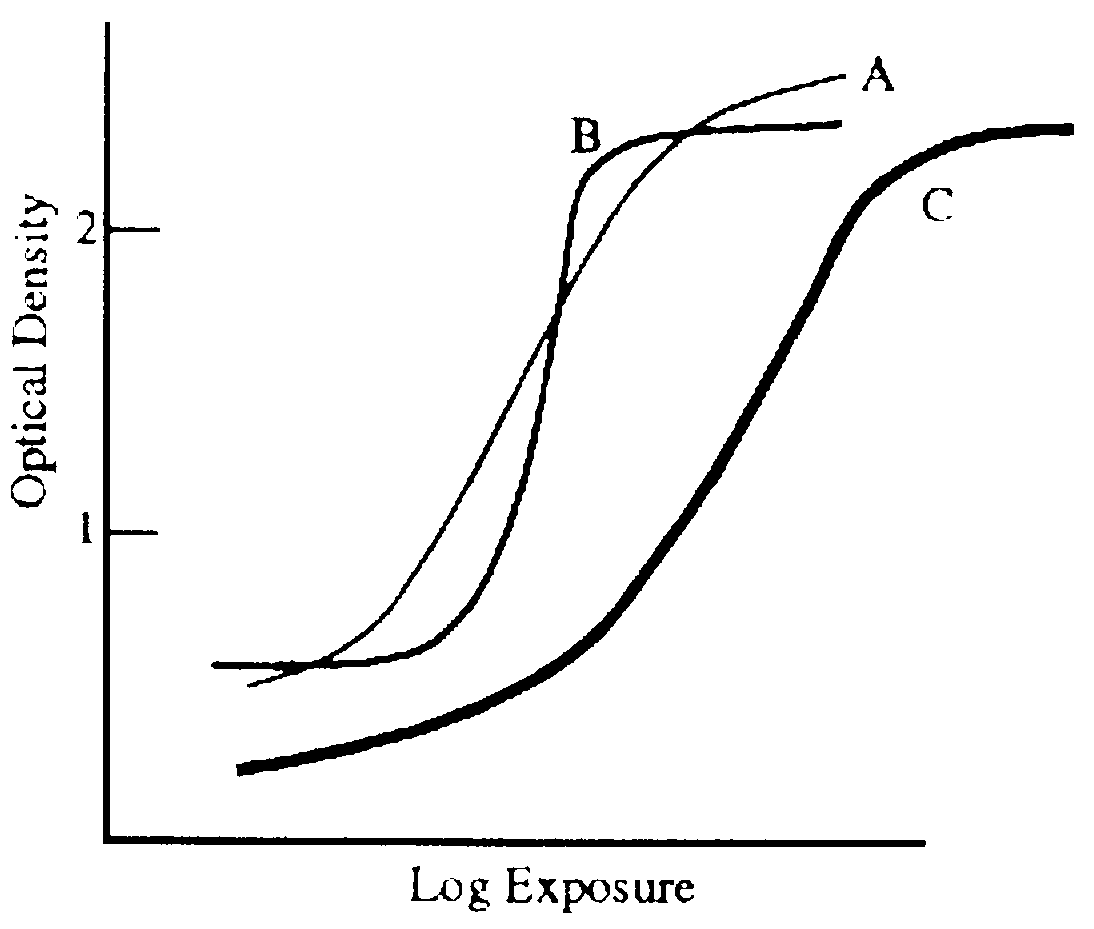
D23. Consider the three characteristic curves in the diagram. Which statement is false?
A. System B has the highest contrast.
B. System C has the widest latitude.
C. System A has the highest maximum density.
D. System B has the highest base-fog density.
E. System C is the fastest.
D24. In some situations, e.g., a chest exam, it is important to see radiographic anatomy in both high- and low-density regions. To aid in this, one could choose a film with a ______
A. High gradient
B. High gamma
C. Slow speed
D. Long latitude
E. Low fog
D25. Which of the following is not a contributing factor to average glandular dose in a mammogram?
A. X-ray tube target material
B. X-ray tube focal spot size
C. kVp applied
D. HVL of the beam
E. Degree of compression
D26. The K-characteristic x-rays of molybdenum target tubes comprise a significant portion of the total x-ray flux. These x-rays have energies predominantly between _____ keV and _____ keV
A. 10, 12
B. 15, 16
C. 17, 20
D. 24, 26
E. 59, 69
D27. A typical half-value layer (HVL) for a screen-film mammographic unit is:
A. 0.03mm Mo
B. 0.30 mm Mo
C. 2.5 mm Al
D. 0.30 mm Al
E. 0.l0 mm Cu
D28. Which grid would be the best choice for use as a stationary grid in mammography?
A. 44 lines/cm, 5:1 ratio
B. 44 lines/cm, 12:1 ratio
C. 80 lines/cm, 5:1 ratio
D. 80 lines/cm, 12:1 ratio
E. Any of the above, as long as they are made of carbon fiber
D29. Which of the following is not true? Vigorous compression in mammography reduces:
A. Patient dose.
B. Scatter.
C. Motion unsharpness.
D. Subject contrast.
D30. The filtration in mammography units primarily transmits the characteristic x-rays. The very low-energy bremsstrahlung x-rays are filtered because they contribute to ______ , and the higher energy bremsstrahlung x-rays are filtered because they contribute to ______
A. tube heating, off-focus radiation
B. heel effect, focal spot blooming
C. radiation dose, loss of contrast
D. grid cut-oft, septal penetration
E. coherent scatter, K-edge photons
D31 -D35. Match the following components to the figure of the image intensifier (II) tube:
D31. Focusing electrode ______
D32. Input screen _______
D33. Photocathode ______
D34. Output screen ______
D35. Vacuumgetter
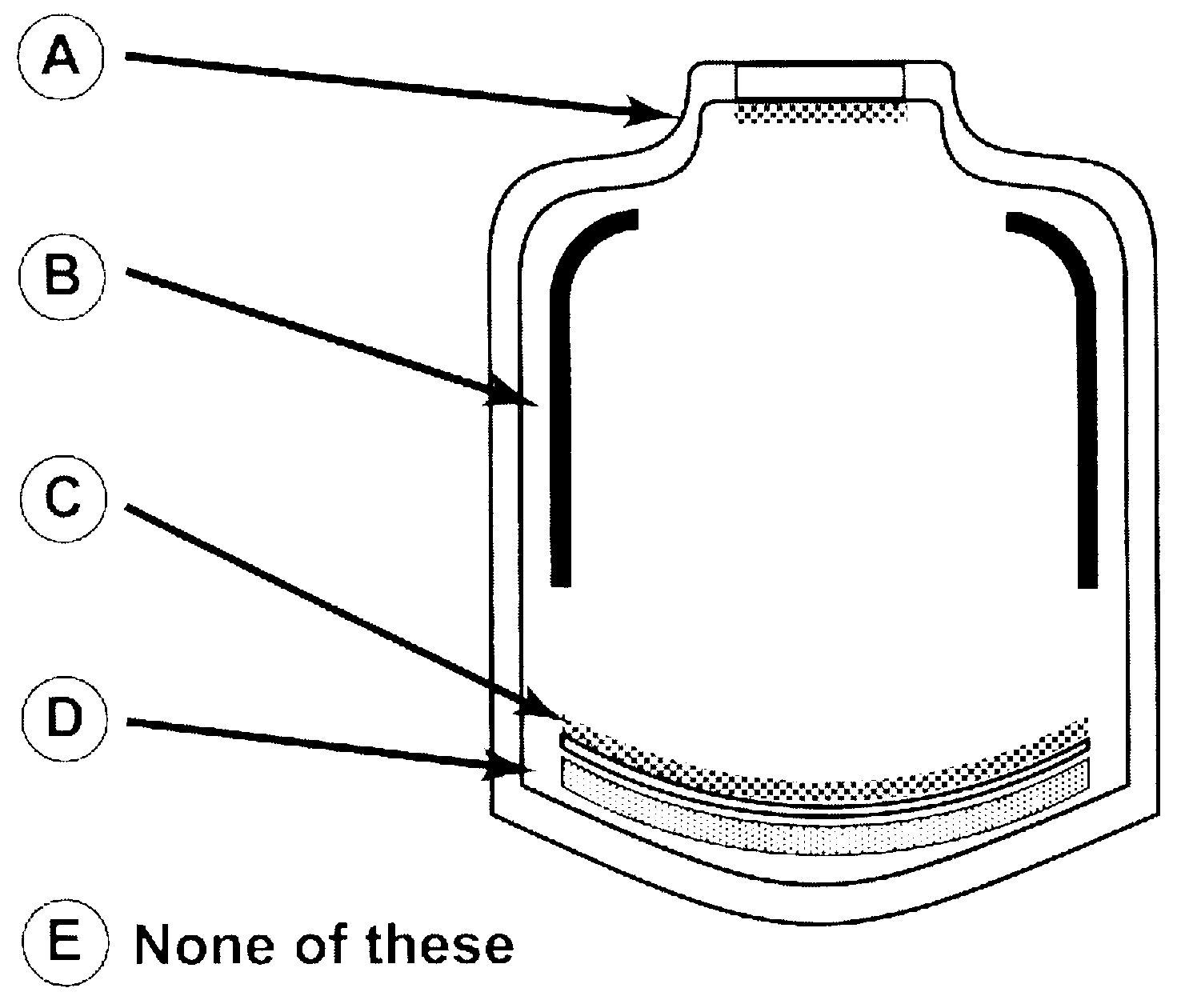
D36. The fluoroscopic operating factors displayed on a monitor are 120 kVp and 10 mA. Which of the following is true?
A. The skin entrance dose is unusually low.
B. The five-minute timer is broken.
C. The skin entrance dose is extremely high.
D. The display must be wrong.
E. The anti-scatter grid is not in the beam.
D3 7. The maximum vertical resolution in lp/mm for a 23-cm input diameter image intensifier coupled to a 1024 line TV system is ______
A. 0.8
B. 1.5
C. 2.2
D. 3.1
E. 4.0
D38. The major differences between fluoroscopy and standard radiography include all of the following except:
A. Focal spot size.
B. Spatial resolution.
C. Tube current.
D. Tube potential.
E. Source-to-skin distance.
D39. The low contrast response (sensitivity) of a CT image as recorded on film is not affected by:
A. Total x-ray exposure.
B. Focal spot size.
C. Slice thickness.
D. Window/level settings.
D40. For CT images, all of the following factors improve the visibility of large, low-contrast lesions except:
A. Smaller pixel sizes.
B. Thicker CT slices.
C. Higher mAs.
D. Smaller patient size.
E. Smooth reconstruction algorithm.
D41 -D42. For a particular CT scanner's beam quality the linear attenuation coefficient for water is 0.20 cm-1 and that for a tumor is 0.22 cm-1. For this scanner:
D41. The CT number of water is ______
A. -1000
B. -200
C. 0
D. 100
E. 200
D41 -D42. For a particular CT scanner's beam quality the linear attenuation coefficient for water is 0.20 cm-1 and that for a tumor is 0.22 cm-1. For this scanner:
D42. The CT number of the tumor is ______
A. -220
B. -100
C. 91
D. 100
E. 200
D43. The major advantage of a CT scanner over a screen-film radiography system is ______
A. Lower radiation dose
B. Higher spatial resolution
C. Less geometrical unsharpness
D. Better low-contrast discrimination
E. Less motion blur
D44. Desirable characteristics of radiation detectors in CT scanners include all of the following factors except:
A. High absorption efficiency.
B. High geometric efficiency.
C. Isotropic response.
D. Fast temporal response.
E. Small size.
D45. The number of 512 x 512 images with 12 bit pixel values that can be stored on a 2 gigabyte optical disk is approximately ______ . (Assume integer byte values at each pixel location.)
A. 5
B. 37
C. 315
D. 4000
E. 5000
D46. In digital imaging, all of the following are true except:
A. 7 bits can represent 512 shades of gray.
B. The resolution of a 512 x 512 display matrix applied to a 10 inch II is 1.0 lp/mm.
C. A 256 x 256 image has 64 K pixels.
D. 1 byte is 8 bits.
D47. Concerning computed radiography (CR), which of the following is true?
A. Numerous, small solid-state detectors are used to capture the x-ray exposure patterns.
B. It has better spatial resolution than film.
C. It is ideal for portable x-ray examinations, when photo timing cannot be used.
D. It is associated with high reject/repeat rates.
E. The image capture, storage, and display are performed by the receiver.
D48. In picture archiving and communications systems (PACS), large-matrix display stations (for digitized radiographs and CR) have all of the following except:
A. A magnification function.
B. Interactive window and level functions.
C. Ability to measure the linear attenuation coefficient accurately.
D. Ability to invert the gray-scale values of the image.
E. Ability to rotate and flip the image.
D49. To store images with 256 shades of gray, each pixel in the image will require:
A. 1 byte.
B. 6 bytes.
C. 8 bytes.
D. 1 bit.
E. 6 bits.
D50. Modern digital computers utilize a number system of zeroes and ones which is called the _______ system.
A. Decimal
B. Boolean
C. Binary
D. Decibel
E. Fractal
D51. A higher intensity MRI signal is produced by:
A. Long T1, long T2.
B. Long T1, short T2.
C. Short T1, long T2.
D. Short T1, shortT2.
D52. In biological tissue, relaxation times are ordered:
A. T1<T2<T2*
B. Tl<T2*<T2
C. T2*<T2<T1
D. T2<T2*<Tl
E. T2<Tl<T2*
D53-D56. Match the following MRI imaging methods with the most appropriate characteristic:
A. Phase encoding in one direction.
B. Phase encoding in two directions.
C. Frequency encoding in two directions.
D. Flip angles less than 90 degrees generally used.
E. Echo generated by a 180 degree RF.
D53. Spin echo imaging
D54. Gradient echo imaging
D55. 2-D FT imaging
D56. 3-D FT imaging
D57. All of the following are MRI artifacts except:
A. Bounce point.
B. Chemical shift.
C. Zipper.
D. Wrap-around.
E. Ring.
D58. Ultrasound moves with the highest velocity in:
medium Z
A. Fat 1.38
B. Blood 1.61
C. Muscle 1.70
D. Bone 7.80
D59. The attenuation of ultrasound in soft tissue, in db/cm-MHz, is:
A. 0.1.
B. 1.0.
C. 10.
D. 100.
E. 1000.
D60. The acoustic impedance of a type of tissue depends on:
A. Ultrasound frequency and tissue viscosity
B. Ultrasound wavelength and tissue density
C. Tissue elasticity and susceptibility
D. Ultrasound velocity and tissue density
D61. The velocity of a 2 MHz ultrasound beam is 1540 m/s in soft tissue. If the frequency is increased to 4 MHz, the _______ will also increase.
A. Velocity
B. Wavelength
C. Acoustical impedance
D. Absorption
E. Viscosity
D62. If an ultrasound beam is attenuated by 99%, the intensity of the original beam to the echo is _______
A. 1 dB
B. 2 dB
C. 20 dB
D. 99 dB
D63. In diagnostic ultrasound using a phased array, the axial resolution depends on the:
A. Number of scan lines used.
B. Imaging depth.
C. Length of the fresnel zone.
D. Transducer diameter.
E. Pulse length.
D64. Reverberation artifacts in ultrasound are caused by:
A. Scattering from small objects
B. Decreased signal intensity in air
C. Multiple reflections from two adjacent interfaces
D. Random signals produced in the electronics of the transducer
E. Patient movement
D65. The largest Doppler ultrasound shifts are from scatterers in ______
A. A large artery
B. Arterial branches
C. The aorta
D. Capillaries
E. Vessel walls
D66. At 9:00 a.m. there are 20.0 mCi of Tc-99m in a syringe. The activity at 12:00 noon is ____ mCi.
A. 10
B. 14.1
C. 15.0
D. 16.2
E. 19
D67. In a Tc generator system, the build-up rate of the daughter is maximum:
A. When parent and daughter are in transient equilibrium.
B. When parent and daughter are in secular equilibrium.
C. Just before elution of the generator.
D. Just after elution of the generator.
D68. Molybdenum breakthrough is assessed for all Tc-99m generator elutions primarily because of:
A. Alumina chemical contamination.
B. Increased patient radiation dose.
C. Differential biodistribution.
D. Different PHA settings required. (Pulse height analyser)
E. Transient equilibrium decay.
D69. Dose calibrators used to assess the amount of activity in nuclear medicine radiopharmaceuticals are affected by all of the following factors except:
A. Source geometry.
B. Background activity.
C. Saturation at high activities.
D. Pulse height analyzer window settings.
E. Electronic drifts.
D70. While imaging a patient with Tc-99m, the multichannel analyzer displays a small peak at 280 keV The most likely cause is:
A. X-rays from photon interactions with the lead collimator.
B. Backscatter.
C. False coincidences arising from pulse pile-up.
D. Molybdenum breakthrough photons.
E. Compton scatter.
D71. A radioactive sample with a relatively long half-life has a count rate of 3340 counts/minute. The sample must be counted for ______ minutes in order to achieve an accuracy of 1% with 68% reliability. (Assume zero background.)
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 10
E. 30
D72. Regarding Anger cameras, all of the following are true except:
A. Resolution increases with the number of photomultiplier tubes per unit area.
B. Resolution increases with increasing collimator thickness.
C. Resolution with a parallel hole collimator increases with decreasing hole diameter.
D. Efficiency increases with decreasing collimator length.
E. High-energy collimators have higher efficiency than low-energy collimators.
D73. The principal function of a photomultiplier tube is to:
A. Absorb gammas and convert their energy to electrons.
B. Convert light to electrons which are then amplified by an avalanche cascade.
C. Amplify light quanta by multiple internal reflections.
D. Supply electrical power to the NaI crystal.
E. Convert gammas to light to form the image.
D74. The intrinsic resolution of a gamma camera is 5 mm. The collimator resolution is 10 mm. The overall system resolution is _______ mm.
A. 15
B. 11.2
C. 7.5
D. 5.0
E. 0.5
D75. In an anterior spot image of the thyroid, a starburst artifact may be seen. The cause of this artifact is:
A. Contamination of the collimator.
B. Imperfections in the evenness of the collimator holes.
C. An image reconstruction artifact caused by filtered back projection.
D. Local photomultiplier tube dead time.
E. Septal penetration.
D76. A patient is imaged using a 256 x 256 matrix on a gamma camera with a 40-cm field of view. The width of each image pixel is ______ mm.
A. 3.12
B. 1.56
C. 1.01
D. 0.96
E. 0.78
D77. Some dedicated PET scanners can perform both 2-D and 3-D scans. The difference is:
A. 2-D scans acquire transaxial images and cannot display coronal or sagittal images.
B. 3-D scans acquire the data directly in coronal or sagittal planes.
C. 2-D scans acquire the data one slice at a time, whereas 3D scans acquire all slices simultaneously.
D. Only 3-D scans can be corrected for attenuation.
E. 2-D scans have septa in front of the detectors to reduce events from scattered photons.
D78. Positron cameras detect:
A. Positrons of the same energy in coincidence.
B. Positrons and electrons in coincidence.
C. Photons of different energies in coincidence.
D. Annihilation photons in coincidence.
D79. The assigned values in each pixel in the reconstructed image of SPECT represent:
A. Densities.
B. Absorption factors.
C. Attenuation factors.
D. Radioisotope concentrations.
D80-D84. In nuclear medicine imaging, match the following quality control procedures with the relevant choice:
A. Gamma camera resolution
B. Gamma camera field uniformity
C. Photopeak window of the pulse height analyzer
D. Dose calibrator linearity
E. Dose calibrator constancy
D80. Checked daily using a uniform flood source.
D81. Checked daily using two standardized long half-life sources.
D82. Checked quarterly by measuring the decay of Tc-99m over 72 hrs or more.
D83. Checked daily by placing a small amount of a known source of radioisotope in front of the camera.
D84. Checked weekly using a bar phantom without a collimator.
D85-D87. Regarding FDA requirements for mammography quality control tests, select the required frequency for each test.
A. Annually
B. Semi-annually
C. Quarterly
D. Weekly
E. Daily
D85. Darkroom fog, screen-film contact, and compression.
D86. Processor quality control and darkroom cleanliness.
D87. Breast entrance exposure and average glandular dose.
D88. If a fluoroscopic procedure delivers an entrance exposure rate of 5 R/min, the scatter exposure rate at the table side 1 meter from a large patient would be about ______
A. 2 R/min
B. 100 mR/sec
C. 300 mR/hr
D. l00 μR/hr
E. 50 mR/sec
D89. Well collimated AP and lateral chest radiographs are taken on a female patient, who later discovers she is pregnant. The dose to the fetus would be about ______ mSv.
A. 0.005
B. 0.5
C. 3
D. 5
E. 20
D90. Interventional radiology procedures require significant fluoroscopy, and can deliver patient entrance doses of up to ______ mGy.
A. 2
B. 20
C. 200
D. 2,000
E. 20,000
D91. In nuclear medicine studies, critical organ doses are usually about ______ Gy.
A. 0.005
B. 0.05
C. 0.5
D. 5
E. 50
D92. The typical amount of lead in lead aprons used in fluoroscopy rooms is about ______
A. l0μm
B. 0.lmm
C. 0.5mm
D. 0.5cm
E. 1.0cm
D93. During a typical fluoroscopy procedure a radiologist wearing a lead apron and no protective eyewear receives a uniform whole body exposure of 20 mR. How many similar procedures can the radiologist perform in one week?
A. 5
B. 15
C. 50
D. 100
E. 250
D94. The principal source of radiation exposure to personnel during fluoroscopy is:
A. Leakage from the x-ray tube housing.
B. Radiation scattered from the patient.
C. Radiation scattered from the image intensifier.
D. Electrons leaking from the image intensifier.
E. Radiation scattered from the walls and floor.
D95-D99. Match the following:
A. Exponential
B. Linear
C. Power function
D. Inverse square
E. Logarithm
D95. Radioactive decay.
D96. Measurement of ultrasound power levels.
D97. Decrease of radiation intensity with distance.
D98. Relation between kVp and x-ray output.
D99. Relation between CT number and linear absorption coefficient.